Contents
- 1 Adderall vs. Ritalin: Differences in Side Effects and Addiction
- 1.0.1 Are Adderall and Ritalin addictive?
- 1.0.2 What is the dosage for Ritalin vs. Adderall?
- 1.0.3 What are the side effects of Adderall vs. Ritalin?
- 1.0.4 What drugs and supplements interact with Adderall vs. Ritalin?
- 1.0.5 In what forms are these drugs available?
- 1.0.6 Are these drugs safe during pregnancy or breastfeeding?
- 1.0.7 From
- 1.0.8 Summary
Adderall vs. Ritalin: Differences in Side Effects and Addiction
Ritalin and Adderall are prescribed central nervous system stimulants for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy.
Both drugs alter norepinephrine and dopamine levels in the brain, improving attention, reducing impulsiveness, enhancing organization, enhancing listening skills, and managing behavioral issues.
These drugs are typically used in conjunction with ADHD treatment programs that may involve counseling and behavioral therapies.
Doctors also prescribe Ritalin and Adderall to combat narcolepsy, a sleep disorder, to promote daytime wakefulness.
However, both drugs have the potential for addiction, misuse, and abuse, which can lead to dependence.
Are Adderall and Ritalin addictive?
Both Ritalin and Adderall can be habit-forming and addictive, even when taken at prescribed doses. Caution should be exercised when prescribing these drugs to individuals with a history of substance abuse. Supervision from a healthcare professional is necessary when withdrawing from either drug, as overdose can result in cardiac arrest and death.
What is the dosage for Ritalin vs. Adderall?
Adderall dosage
Adderall is typically taken once or twice daily, with doses spaced at least 4-6 hours apart. The recommended daily dose varies from 2.5 to 60 mg, depending on the patient’s age and condition.
Adderall XR is taken once daily, with a recommended dose of 5-40 mg administered in the morning. The contents of Adderall XR capsules can be sprinkled onto applesauce and consumed immediately. To avoid insomnia, amphetamines should only be taken during waking hours, with late evening doses avoided.
Ritalin, Ritain XR dosage
The dose of Ritalin should be adjusted based on individual responses. It can be given once, twice, or thrice daily, depending on the formulation. The recommended dose for Concerta is 18-72 mg taken once daily.
The recommended dose for Ritalin LA is 10-60 mg once daily. As for regular Ritalin, the recommended dose is 10-60 mg daily, divided into 2 or 3 doses.
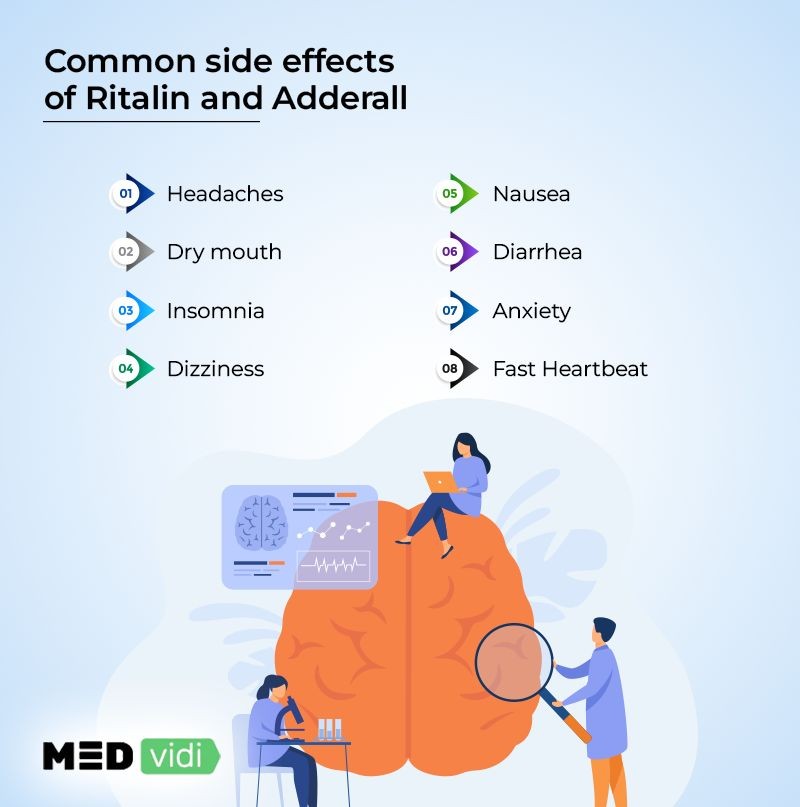
What are the side effects of Adderall vs. Ritalin?
Adderall side effects
Amphetamines, such as Adderall, can cause excessive stimulation of the nervous system, resulting in the following side effects:
- Nervousness
- Restlessness
- Excitability
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Insomnia
- Fear
- Anxiety
- Hallucinations
- Tremor
- Convulsions (seizures)
- Increased blood pressure and heart rate, potentially leading to heart palpitations
Additional side effects include:
- Sudden death
- Stroke
- Heart attack
- Depression
- Manic episodes
- Aggressive behavior or hostility
- Psychosis
- Growth suppression (with long-term use)
- Dependence
- Withdrawal symptoms
Priapism, a painful and prolonged penile erection lasting over 4 hours, has been reported in patients receiving stimulants. Medical attention should be sought immediately if priapism is suspected.
Ritalin side effects
The most common side effects of Ritalin include:
Insomnia can be minimized by taking the drug before noon. For children with ADHD, the most prevalent side effects are loss of appetite, abdominal pain, weight loss, and sleep disturbances. The incidence and severity of these side effects are lower compared to dextroamphetamine (Dexedrine).
Other notable side effects of Ritalin include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Dizziness
- Palpitations
- Headache
- Chest pain
- Involuntary movements
- Increased heart rate
- Increased blood pressure
- Psychosis
Rare cases of Tourette’s syndrome, characterized by uncontrollable tics like grimacing, have been reported with Ritalin use. Caution is advised when prescribing Ritalin to patients with Tourette’s syndrome or a family history of the condition, as well as those with severe anxiety, seizures, psychosis, emotional instability, major depression, glaucoma, or motor tics.
Gradual withdrawal, under medical supervision, is recommended to avoid depression following long-term Ritalin therapy.
Similar to Adderall, priapism has been reported in pediatric and adult patients treated with Ritalin, necessitating prompt medical attention.
What drugs and supplements interact with Adderall vs. Ritalin?
The stimulant effects of Ritalin on the central nervous system can be intensified when combined with other CNS stimulants, such as caffeine and certain cough-and-cold medications containing pseudoephedrine or phenylpropanolamine.
Ritalin and Adderall should not be used in conjunction with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) like isocarboxazid, phenelzine, tranylcypromine, and procarbazine, as this can result in a hypertensive crisis (severe high blood pressure). Ritalin should not be taken within 14 days of using an MAOI.
Ritalin may diminish the blood pressure-lowering effects of antihypertensive medications, necessitating careful monitoring when initiating or discontinuing Ritalin in patients taking antihypertensive drugs.
Antacids can increase the absorption and effectiveness of amphetamine salts, thereby enhancing their side effects.
By submitting, I acknowledge and accept MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy, and understand that I can unsubscribe from MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.
In what forms are these drugs available?
Adderall is available in the following forms and preparations:
- Adderall tablets: 5, 7.5, 10, 12.5, 15, 20, and 30 mg
- Adderall XR capsules: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 mg
Ritalin is available in the following forms and preparations:
- Tablets: 5, 10, and 20 mg
- Sustained-release tablets (Ritalin SR): 20 mg
- Long-acting tablets (Ritalin LA): 20, 30, and 40 mg
- Extended-release tablets (Concerta): 18, 27, 36, and 54 mg
- Chewable tablets (Methylin): 2.5, 5, and 10 mg
- Solution (Methylin): 5 mg/5 ml, 10 mg/5 ml
- Extended-release tablets (Methylin ER, Metadate ER): 10, 20 mg
- Extended-release capsules (Metadate): 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, and 60 mg
Are these drugs safe during pregnancy or breastfeeding?
- Pregnant women should avoid using amphetamines like Adderall. Infants born to mothers dependent on amphetamines may experience withdrawal symptoms and have an increased risk of low birth weight.
- There are insufficient studies on the safety of Ritalin in pregnant women.
- Since Ritalin and Adderall are excreted in breast milk, their safety during breastfeeding is unknown. Therefore, caution is advised when using these drugs while breastfeeding.
From
ADHD Resources
Featured Centers
- What Are the Best PsA Treatments for You?
- Understanding Biologics
- 10 Things People With Depression Wish You Knew
Summary
Adderall (dextroamphetamine, amphetamine) and Ritalin (methylphenidate) are central nervous system stimulants prescribed to children and adults with ADHD. Side effects of these drugs include nervousness, agitation, anxiety, stomach ache, vision problems, nausea, vomiting, palpitations, insomnia, increased blood pressure, loss of appetite, weight loss, headache, dizziness, tremor, weakness, diarrhea, constipation, fear, restlessness, excitability, irritability, fever, hair loss, difficulties with orgasm, sweating, rash, psychosis, numbness or tingling, cold hands and feet, aggression, growth suppression, seizures, prolonged and painful erections, vasculitis, peripheral vasculopathy, and Raynaud’s phenomenon.