Contents
- 1 Acetaminophen (Tylenol) vs. Ibuprofen (Advil) for Pain (Differences in Side Effects and Dosage)
- 1.0.1 How do acetaminophen and ibuprofen work (mechanism of action)? What are they used for?
- 1.0.2 Which one is better for pain relief, acetaminophen or ibuprofen?
- 1.0.3 What are the side effects of acetaminophen vs. ibuprofen?
- 1.0.4 What is the dosage for acetaminophen vs. ibuprofen?
- 1.0.5 What drugs interact with acetaminophen vs. ibuprofen?
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) vs. Ibuprofen (Advil) for Pain (Differences in Side Effects and Dosage)
The most common brand name for acetaminophen is Tylenol. Some brand names for ibuprofen include Advil and Motrin.
How do acetaminophen and ibuprofen work (mechanism of action)? What are they used for?
Acetaminophen belongs to a class of drugs called analgesics and antipyretics. It reduces the production of prostaglandins in the brain, which cause inflammation and swelling. Acetaminophen elevates the pain threshold, requiring a greater amount of pain to be felt. It also lowers body temperature when it is elevated.
Ibuprofen belongs to a class of drugs called nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). It blocks the enzyme that makes prostaglandins, reducing inflammation, pain, and fever.
Which one is better for pain relief, acetaminophen or ibuprofen?
Which is better, acetaminophen or ibuprofen?
Acetaminophen uses
- Acetaminophen is used for pain relief and reducing fever and aches associated with many conditions.
- It relieves pain in mild arthritis but has no effect on underlying inflammation, redness, and swelling.
- If the pain is not due to inflammation, acetaminophen is as effective as aspirin.
- It is as effective as NSAIDs like ibuprofen for relieving pain in osteoarthritis of the knee.
Acetaminophen should not be used for longer than 10 days unless directed by a doctor.
Ibuprofen uses
Ibuprofen is used for the treatment of mild to moderate pain, inflammation, and fever caused by various diseases, including:
- menstrual cramps,
- osteoarthritis,
- rheumatoid arthritis,
- juvenile idiopathic arthritis,
- inflammatory conditions,
- minor pain of arthritis,
- reduces temporary fever,
- headaches,
- cramps,
- back pain,
- joint pain,
- the common cold,
- toothaches,
- minor aches and pains,
- strains, and
- sprains.
What are the side effects of acetaminophen vs. ibuprofen?
Acetaminophen side effects
Side effects with acetaminophen are not common.
The most common side effects are:
Other important side effects include:
- Hypersensitivity reactions
- Serious skin reactions
- Kidney damage
- Anemia
- Reduced number of platelets in the blood
- Chronic alcohol use may increase the risk of stomach bleeding.
The most serious side effect is liver damage due to large doses and chronic or concomitant use with alcohol or other drugs that also damage the liver.
Ibuprofen side effects
- The most common side effects from ibuprofen are: rash, ringing in the ears, headaches, dizziness, drowsiness, abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, and heartburn.
- NSAIDs reduce blood clotting and increase bleeding after injury.
- Ibuprofen may cause ulceration of the stomach or intestine. Ulcers may bleed and can occur without abdominal pain, resulting in black stool, weakness, and dizziness upon standing.
- NSAIDs reduce blood flow to the kidneys and impair kidney function. Caution should be taken in patients with impaired kidney function or congestive heart failure.
- People who are allergic to other NSAIDs, including aspirin, should avoid ibuprofen.
- Other serious side effects associated with NSAIDs are: fluid retention, blood clots, heart attacks, hypertension, and heart failure.
- NSAIDs increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, and related conditions in people with or without heart disease or risk factors for heart disease. NSAIDs should not be used for pain resulting from coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery.
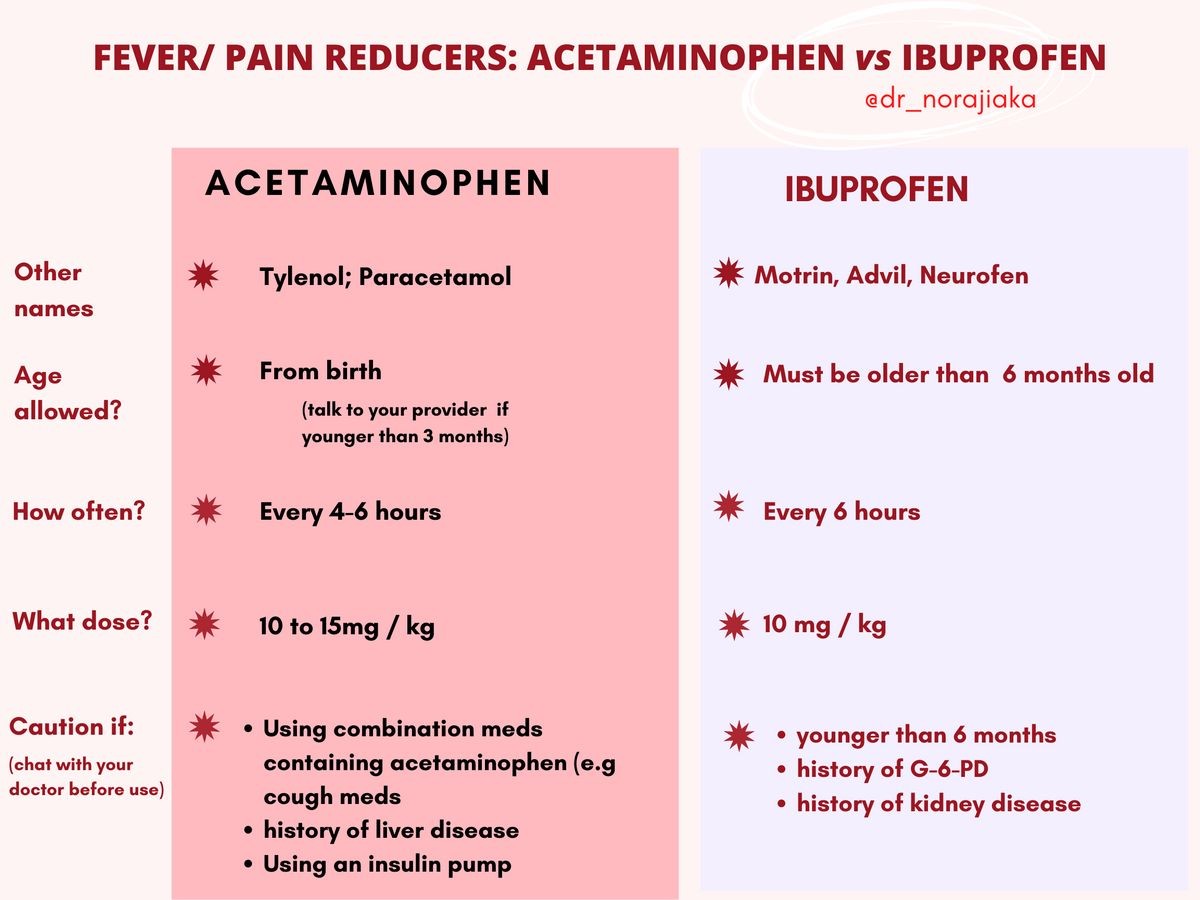
What is the dosage for acetaminophen vs. ibuprofen?
Acetaminophen dosage
- The dose for adults is 325 to 650 mg every 4 hours or 500 mg every 8 hours with immediate release formulations.
- The dose for extended release caplet is 1300 mg every 8 hours.
- The maximum daily dose is 4 grams.
- The oral dose for a child depends on age and weight. The dosing is 10-15 mg/kg every 6-8 hours not to exceed 2.6 g/day for children under 12 years. For children 12 years and older, the dose is 40-60 mg/kg/day every 6 hours not to exceed 3.75 g/day.
Ibuprofen dosage
- For minor aches, mild to moderate pain, menstrual cramps, and fever, the usual adult dose is 200 or 400 mg every 4 to 6 hours.
- Arthritis is treated with 300 to 800 mg 3 or 4 times daily.
- Under the care of a physician, the maximum dose is 3.2 g daily. Otherwise, the maximum dose is 1.2 g daily.
- Ibuprofen should not be used for more than 10 days for pain or more than 3 days for a fever unless directed by a physician.
- Children 6 months to 12 years of age are usually given 5-10 mg/kg of ibuprofen every 6-8 hours. The maximum dose is 40 mg/kg daily.
- Juvenile arthritis is treated with 20 to 40 mg/kg/day in 3-4 divided doses.
- Ibuprofen should be taken with meals to prevent stomach upset.
What drugs interact with acetaminophen vs. ibuprofen?
Acetaminophen drug interactions
Acetaminophen is metabolized by the liver and can interact with drugs that increase liver enzyme action, such as carbamazepine, isoniazid, and rifampin. These drugs can reduce the levels and effectiveness of acetaminophen. Large doses and concomitant use with alcohol or other drugs that harm the liver may cause severe liver damage. Cholestyramine reduces the effect of acetaminophen by decreasing its absorption from the intestines. Therefore, the two medications should be taken at different times. Acetaminophen doses greater than 2275 mg per day may increase the blood thinning effect of warfarin. Hence, prolonged administration or large doses of acetaminophen should be avoided during warfarin therapy.
Ibuprofen drug interactions
Ibuprofen is associated with several interactions that can affect the action of other drugs. It may increase blood levels of lithium, reduce blood pressure-lowering effects of antihypertensive drugs, increase blood levels of methotrexate and aminoglycosides, worsen kidney function affected by cyclosporine, interact with oral blood thinners, increase the risk of ulcer when taken with aspirin, increase the risk of stomach ulcers in individuals who consume more than three alcoholic beverages per day, and increase the likelihood of upper gastrointestinal bleeding when combined with SSRIs or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.


