Contents
Body Mass Index (BMI) Calculator
BMI values are based on clinical data about average measurements across a wide range of people.
The BMI calculator provides general ranges of healthy and unhealthy weights for adults based on height. It does not consider individual conditions. Moreover, it does not distinguish fat from muscle, water, or bone, making it less helpful in identifying health problems related to weight.
This BMI calculator allows you to screen yourself for obesity or unhealthy weight. If your results aren’t in the healthy range, don’t worry. People with muscular builds may be classified as obese even with a low body fat percentage and optimum health simply because the BMI formula uses only two data points.
Doctors and researchers use the BMI formula to screen for obesity but not to diagnose it because the BMI is a blunt instrument. It is defined as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared (kg/m2). It can also be calculated for weight in pounds and height in inches.
Body mass index is closely related to body fat percentage but is easier to measure. It is used by many primary care doctors to identify obesity. The higher your BMI, the higher your risk of health problems related to excess weight.
Are weight-for-height tables useful to determine obesity?
Measuring body fat percentage can be difficult, so other methods are often relied upon to diagnose obesity. Two widely used methods are weight-for-height tables and BMI. While both measurements have limitations, they are reasonable indicators of weight problems. The calculations are easy, and no special equipment is required.
Most people are familiar with weight-for-height tables. In 1943, the Metropolitan Life Insurance Company introduced their table based on policyholders’ data. Doctors and nurses have used these tables for decades to determine if someone is overweight. The tables usually have a range of acceptable weights for a given height.
The problem with weight-for-height tables is that doctors disagree over the best table to use. Several versions are available, with different weight ranges, and some account for frame size, age, and sex, while others do not.
A significant limitation of all weight-for-height tables is that they do not distinguish between excess fat and muscle. A very muscular person may be classified as obese according to the tables.
What is the body mass index?
The body mass index (BMI) is a measurement used by physicians and researchers studying obesity.
The BMI uses a mathematical formula that accounts for weight and height.
The BMI measurement has some problems. Not everyone agrees on the cutoff points for "healthy" versus "unhealthy" BMI ranges. It also does not provide information on a person’s percentage of body fat. However, BMI is a useful general guideline and is a good estimator of body fat for most adults 19 to 70 years of age. It may not be an accurate measurement of body fat for bodybuilders, certain athletes, and pregnant women.
BMI equals weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared (BMI = kg/m2). To calculate BMI using pounds, divide weight in pounds by the height in inches squared and multiply by 703.
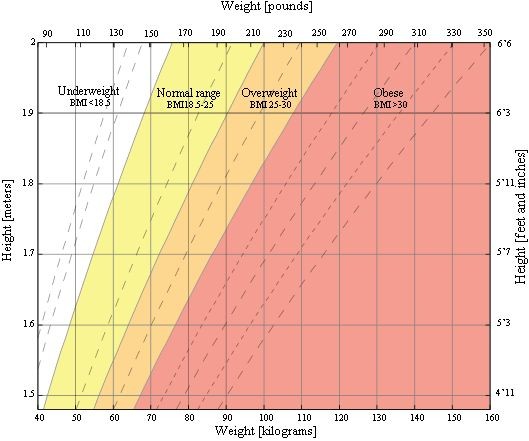
It is important to understand what "healthy weight" means. Healthy weight is defined as a BMI equal to or greater than 19 and less than 25 among all people 20 years of age or over. Obesity is defined as a BMI equal to or greater than 30, which approximates 30 pounds of excess weight.
The World Health Organization uses the BMI to define overweight and obesity using a classification system.
A BMI of 25 to 29.9 is "pre-obese." A BMI of 30 to 34.99 is "obese class I." A BMI of 35 to 39.99 is "obese class II." A BMI of 40.00 or greater is "obese class III."
What can’t your BMI tell you?
Assessment of obesity considers not only how much fat a person has, but also where that fat is located on the body. Body fat distribution differs between men and women.
Women tend to collect fat in their hips and buttocks, resulting in a "pear" shape figure. Men usually collect fat around the belly, resulting in an "apple" shape figure. However, there are exceptions to this rule.
Apple-shaped individuals with fat concentrated in the abdomen are more likely to develop health problems associated with obesity. While any kind of obesity is a health risk, it is better to have a pear shape than an apple shape.
Doctors use a measurement called waist-to-hip ratio to determine whether someone is an apple or a pear. To find out a person’s waist-to-hip ratio, measure the waist at its narrowest point, and then measure the hips at the widest point. Divide the waist measurement by the hip measurement. For example, a woman with a 35-inch waist and 46-inch hips would have a waist-to-hip ratio of 0.76 (35 divided by 46 = 0.76).
Women with waist-to-hip ratios of more than 0.8 and men with waist-to-hip ratios of more than 1.0 are considered "apples."
Another rough way of estimating the amount of abdominal fat is by measuring waist circumference. Men with a waist circumference of 40 inches or greater and women with a waist circumference of 35 inches or greater are considered to have increased health risks related to obesity.
Body mass index vs. body fat percentage
While the BMI is useful as a screening tool, it’s only based on weight and height relative to age, which doesn’t provide enough data points. For instance, a bodybuilder with little body fat may have an "unhealthy" BMI score. Measuring individual body fat percentage gives healthcare professionals an accurate reading of the risk for obesity-related disease.
Actually measuring body fat percentage is not easy and often inaccurate without careful monitoring of the methods. Some methods require special equipment, trained personnel, and are only available in certain research facilities.
- Underwater weighing (hydrostatic weighing): This method weighs a person underwater to calculate lean body mass and body fat. It is one of the most accurate methods, but the equipment is costly.
- BOD POD: The BOD POD is a computerized, egg-shaped chamber. It measures a subject’s mass and volume to determine whole-body density. From this data, body fat and lean muscle mass can be calculated.
- DEXA: Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) measures bone density and the percentage and distribution of body fat in the body using X-rays.
Two simpler and straightforward methods are:
- Skin calipers: This method measures the thickness of the layer of fat just under the skin and uses the results to calculate the percentage of body fat.
- Bioelectric impedance analysis (BIA): BIA involves either standing on a special scale with footpads or using electrodes placed on a wrist, ankle, hand, and foot to measure body fat percentage.