Contents
What Causes Floating-Harbor Syndrome?
Floating-Harbor syndrome is a rare condition characterized by low proportional height with delayed bone age, distinctive facial appearance, and delayed speech development. The cause of this condition is unknown, but it is believed to be a result of a genetic mutation.
Causes of Floating-Harbor Syndrome
Based on existing studies, the exact causes of Floating-Harbor syndrome are not fully understood. However, research suggests that certain traits may contribute to the development of this syndrome.
- Genetics: Medical professionals believe that Floating-Harbor syndrome is caused by heterozygous mutations in the SRCAP gene. This gene regulates the production of the SNF2 protein, which connects to the CREBBP activator protein. Mutations in the SRCAP gene may alter the SNF2 protein, interfering with the normal activation of the CREBBP gene and causing developmental issues.
- In some families, Floating-Harbor syndrome is inherited through autosomal dominant inheritance, meaning it can be passed down from an affected parent. In other cases, the inheritance pattern may be autosomal recessive.
- Floating-Harbor syndrome affects both sexes, but women are more commonly affected.
Further research is needed to determine the exact causes and risk factors of Floating-Harbor syndrome.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Floating-Harbor Syndrome?
Although there are established core symptoms, much is still unknown about this condition due to various factors. Facial abnormalities are a defining characteristic of Floating-Harbor syndrome.
Signs and Symptoms of Floating-Harbor Syndrome
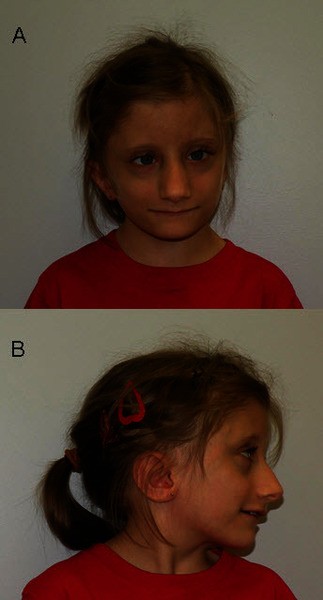
- Facial features: Individuals with Floating-Harbor syndrome may have deep-set eyes, a triangular face, a wide mouth with a thin upper lip, a long nose with a narrow bridge and broad base, low-set ears, abnormally long eyelashes, thin lips, a broad linear mouth, and a prominent triangular-shaped nose.
- Speech-related symptoms include dysarthria, verbal dyspraxia, hypernasality, and high-pitched voices.
- Other symptoms may include delayed bone age, skeletal anomalies, short fingers and toes, short stature, delayed growth, unpredictable and aggressive outbursts, hyperactivity, short attention span, intellectual and learning disabilities, early entry into puberty, dental problems, visual impairment, and various other medical conditions and abnormalities.
Floating-Harbor syndrome causes a wide range of symptoms, with short stature being particularly noticeable. Affected individuals typically grow to a height of 140 cm or less.
How is Floating-Harbor Syndrome Diagnosed?
Floating-Harbor syndrome can often be diagnosed based on the characteristic anatomical anomalies. Doctors and parents can identify these malformations during early childhood. Molecular genetic testing, along with assessment of facial symptoms, can confirm the diagnosis.
Diagnosing Floating-Harbor Syndrome
- Physical and medical history: The attending physician examines the symptoms and medical history, including family history, during the initial consultation.
- Genetic testing, such as sequence analysis, can detect mutations in the SRCAP gene.
- Preimplantation genetic testing may be an option for individuals with known genetic abnormalities. This testing is performed on embryos created through in vitro fertilization.
What are the Treatment Options for Floating-Harbor Syndrome?
Currently, there is no known cure for Floating-Harbor syndrome. Treatment primarily focuses on managing the symptoms and features of the condition.
Managing Symptoms of Floating-Harbor Syndrome
- Early developmental intervention is crucial to help affected children reach their potential.
- Occupational, physical, and speech therapy are often beneficial.
- Additional medical, social, and vocational services may be necessary.
- Counseling and support for parents, as well as genetic counseling, can be helpful.
- Growth hormone therapy may be used in some cases.
- Additional therapies may be recommended based on specific symptoms, and clinical trials may be an option for those with progressive conditions.
Floating-Harbor syndrome is managed through symptom-based treatments, and affected individuals often receive special education and support.
What is the Life Expectancy of People with Floating-Harbor Syndrome?
Due to the severity of symptoms, the prognosis for Floating-Harbor syndrome is generally poor. Short stature, language difficulties, and facial changes are common long-term effects. Gene therapy may offer potential for improving the prognosis in the future.
Although living with Floating-Harbor syndrome can be challenging, many individuals can lead relatively independent lives. Regular examinations may be necessary to address complications.


