Contents
What Are the 4 Stages of Hypertension?
Learn the four stages of hypertension: normal, elevated blood pressure, stage I hypertension, and stage II hypertension.
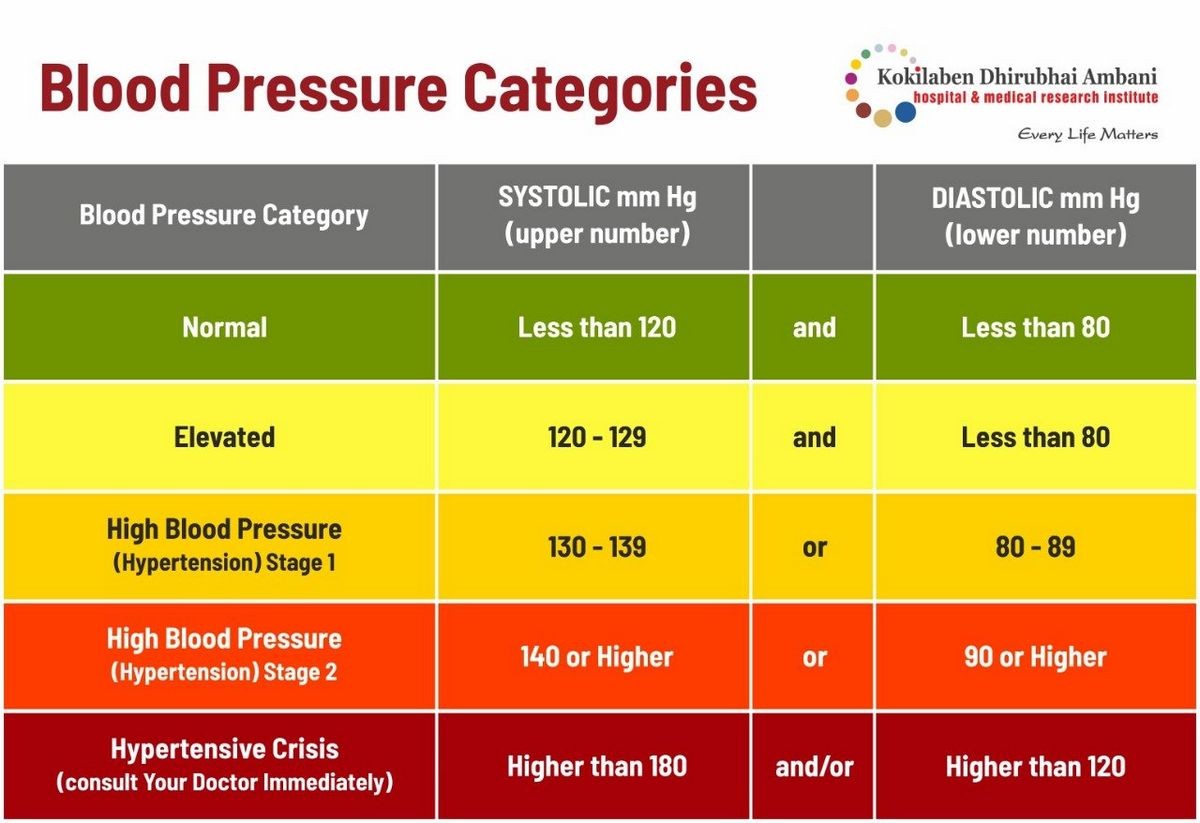
The four stages of hypertension include:
- Normal:
- Systolic pressure less than 120 mmHg and diastolic pressure less than 80 mmHg.
- No need for drugs, but follow a healthy lifestyle and regularly monitor blood pressure.
- Elevated blood pressure:
- Systolic blood pressure between 120 and 129 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure not above 80 mmHg.
- Identifies people at risk of developing stage I or stage II hypertension in the future.
- No medication required, but consider lifestyle changes.
- Stage I hypertension:
- Systolic blood pressure between 130 and 139 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure between 80 and 89 mmHg.
- Doctor may prescribe antihypertensive medications and suggest lifestyle changes.
- Stage II hypertension:
- Systolic pressure exceeds 140 mmHg and diastolic pressure exceeds 90 mmHg.
- To prevent complications like cardiac and stroke issues, multiple drugs, lifestyle changes, diet, and exercise may be recommended.
According to new guidelines, about 46 percent of adults in the United States are classified as having high blood pressure.
A hypertensive crisis is a systolic pressure greater than 180 mmHg or a diastolic pressure greater than 120 mmHg. Contact your doctor if you notice these readings.
What are the different types of hypertension?
Primary hypertension or essential hypertension
- Most hypertensive adults have this type.
- No specific cause identified despite years of research.
- Believed to be caused by genetics, diet, lifestyle, and age.
- Diet and lifestyle changes can reduce blood pressure and risk of complications.
Secondary hypertension
- Occurs when hypertension is caused by an identifiable and potentially reversible cause.
- Accounts for only about 5 to 10 percent of all cases, more common in younger people.
- Caused by factors like narrowed arteries, adrenal gland disease, medication side effects, sleep apnea, hormone/thyroid abnormalities, and aorta narrowing.
Subtypes within primary or secondary hypertension include:
- Resistant hypertension:
- Difficult to control high blood pressure that requires multiple medications.
- Indicates potential secondary cause and may be successfully treated with a combination of drugs or identification of the cause.
QUESTION
Is hypertension curable?
No, hypertension is not curable. It is a chronic disease with an unknown cause in 90 percent of patients. However, it is treatable with medication and lifestyle modifications, requiring regular medical attention and follow-ups with your doctor.
To control hypertension, adopt a healthy lifestyle:
- Balance diet
- Quit smoking
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Reduce sodium intake
- Manage stress levels
- Ensure enough sleep
- Maintain body weight and waistline
- Regular exercise
- Reduce added sugar and refined carbs
- Practice breathing exercises and meditation
Hypertension is usually treated with thiazide diuretics, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers, and calcium channel blockers. If these are ineffective, other medications may be prescribed.
11 complications of hypertension
Hypertension causes complications and problems with the heart, blood vessels, and more:
- Chest pain
- Stroke
- Dementia
- Transient ischemic attack
- Mild cognitive impairment
- Renal diseases
- Eye problems
- Type II diabetes
- Sexual dysfunction
- Bone loss
- Sleep troubles
Regular blood pressure monitoring is critical to detect hypertension early because it is often asymptomatic. Take precautions to prevent complications and follow your doctor’s advice.
Always see your doctor regularly and take medications as prescribed. Monitor blood pressure at home regularly.