Contents
What Are the 4 Types of Shock?
The four types of shock include distributive shock, cardiogenic shock, hypovolemic shock, and obstructive shock.
Shock disrupts the body’s physiology and causes reduced tissue perfusion.
The four main categories of physiological shock are:
What is distributive shock?
Distributive shock is characterized by a drop in peripheral vascular resistance and hypotension.
6 subclassifications of distributive shock
- Septic shock
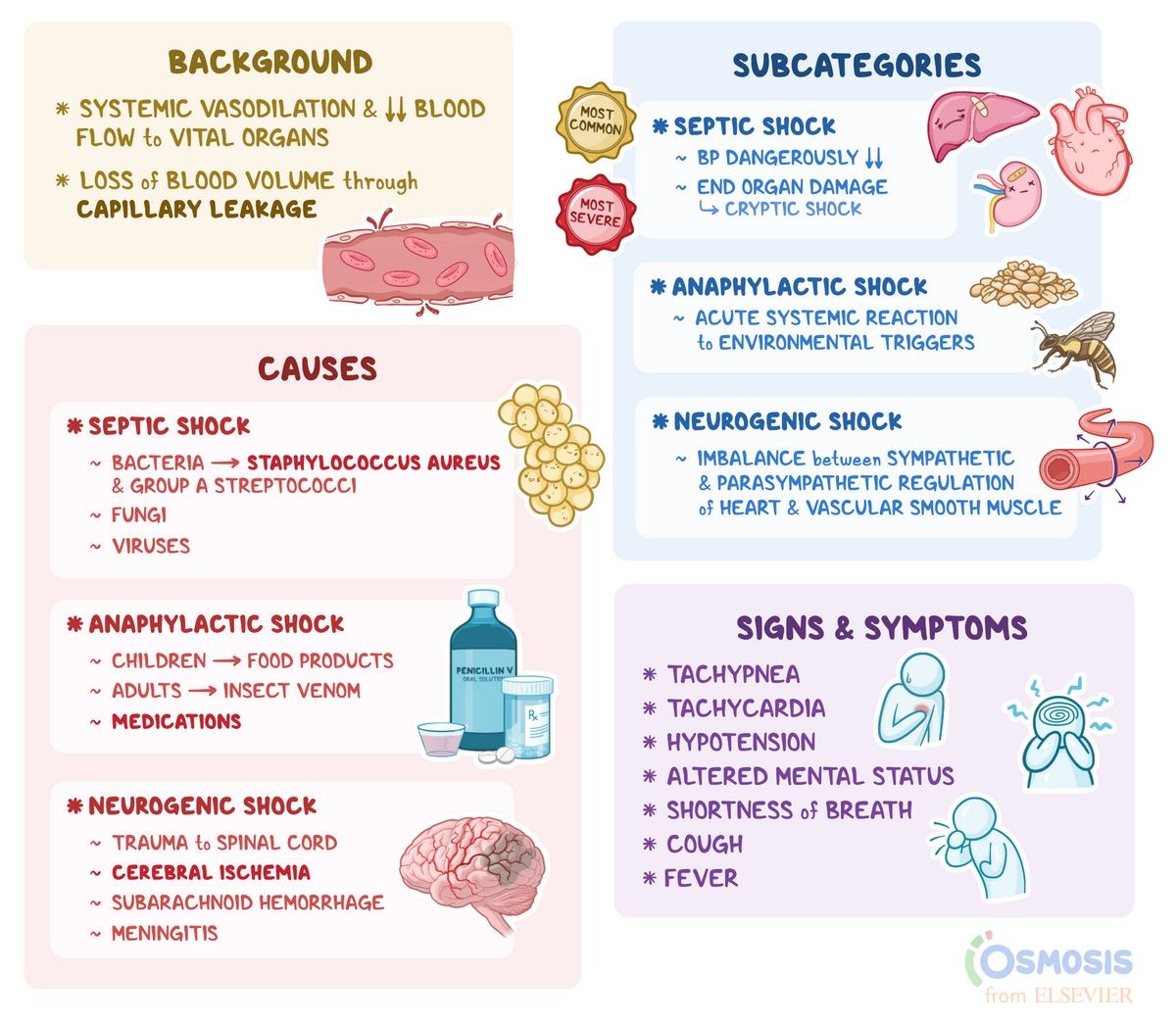
- Septic shock occurs when blood pressure drops dangerously low following an infection.
- The infection might be caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses.
- Toxins created by bacteria can trigger an inflammatory cascade in the body, affecting organ function and causing fluids to leak into surrounding tissues.
- This impairs the heart’s ability to pump blood to organs, lowering blood pressure and preventing blood from reaching key organs.
- Septic shock is mostly seen in conditions with compromised immunity, such as neonatal sepsis, elderly individuals, those with chronic illnesses, or individuals on immunosuppressants.
- Neurogenic shock
- Neurogenic shock occurs due to a lack of equilibrium between parasympathetic and sympathetic stimulation.
- It is typically seen after a severe spinal cord injury or serious brain damage.
- Understanding the changes that occur during neurogenic shock can aid in proper resuscitation efforts.
- Anaphylactic shock
- Anaphylactic shock is a severe life-threatening condition caused by a reaction to an antigenic stimulus.
- Common triggers include food, medications, and insect venom.
- Endocrine shock
- Adrenal failure and myxedema can cause hypotension and shock.
- Hormonal imbalances and myocardial depression can contribute to hypotension and shock.
- Drug and toxin-induced shock
- Overdoses of drugs, venomous bites, transfusion reactions, and infections can cause shock or systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
- Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)
- SIRS is a clinical syndrome defined by a strong inflammatory response.
- Most patients with SIRS in the emergency room are closely monitored for disease severity.
What is cardiogenic shock?
Cardiogenic shock is a condition where the circulatory system fails due to decreased cardiac output caused by heart failure.
Acute myocardial infarction is the most common cause of cardiogenic shock.
Cardiogenic shock can cause severe cellular and metabolic malfunction, organ dysfunction, and death.
3 subclassifications of cardiogenic shock
- Cardiomyopathy
- The shock is caused by cardiomyopathic conditions such as myocardial infarction or acute heart failure.
- Arrhythmic
- Abnormal heart rhythms can cause hypotension and shock.
- Severe rhythm disruptions can lead to cardiac arrest.
- Mechanical
- Severe valve insufficiency or valvular defects can result in cardiogenic shock.
Other causes of cardiogenic shock include ventricular septal abnormalities and ruptured ventricular free wall aneurysms.
What is hypovolemic shock?
Hypovolemic shock occurs due to decreased intravascular volume or decreased preload, which lowers cardiac output.
Hypovolemic shock can be caused by hemorrhage or fluid loss.
- Hemorrhagic shock
- Blood loss from trauma is a common cause of hemorrhagic shock.
- Gastrointestinal bleeding can also lead to hemorrhagic shock.
- Non-hemorrhagic shock
- Fluid loss from various causes can result in non-hemorrhagic shock.
- These causes include diarrhea, vomiting, burns, and obstructive conditions.
What is obstructive shock?
Obstructive shock is caused by extracardiac factors that lead to cardiac pump failure.
2 categories of obstructive shock
- Pulmonary vascular
- Right ventricular failure due to pulmonary embolism or severe pulmonary hypertension is a common cause of obstructive shock.
- Mechanical
- Obstructive shock can also occur due to mechanical causes such as pericardial tamponade or tension pneumothorax.