Types of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
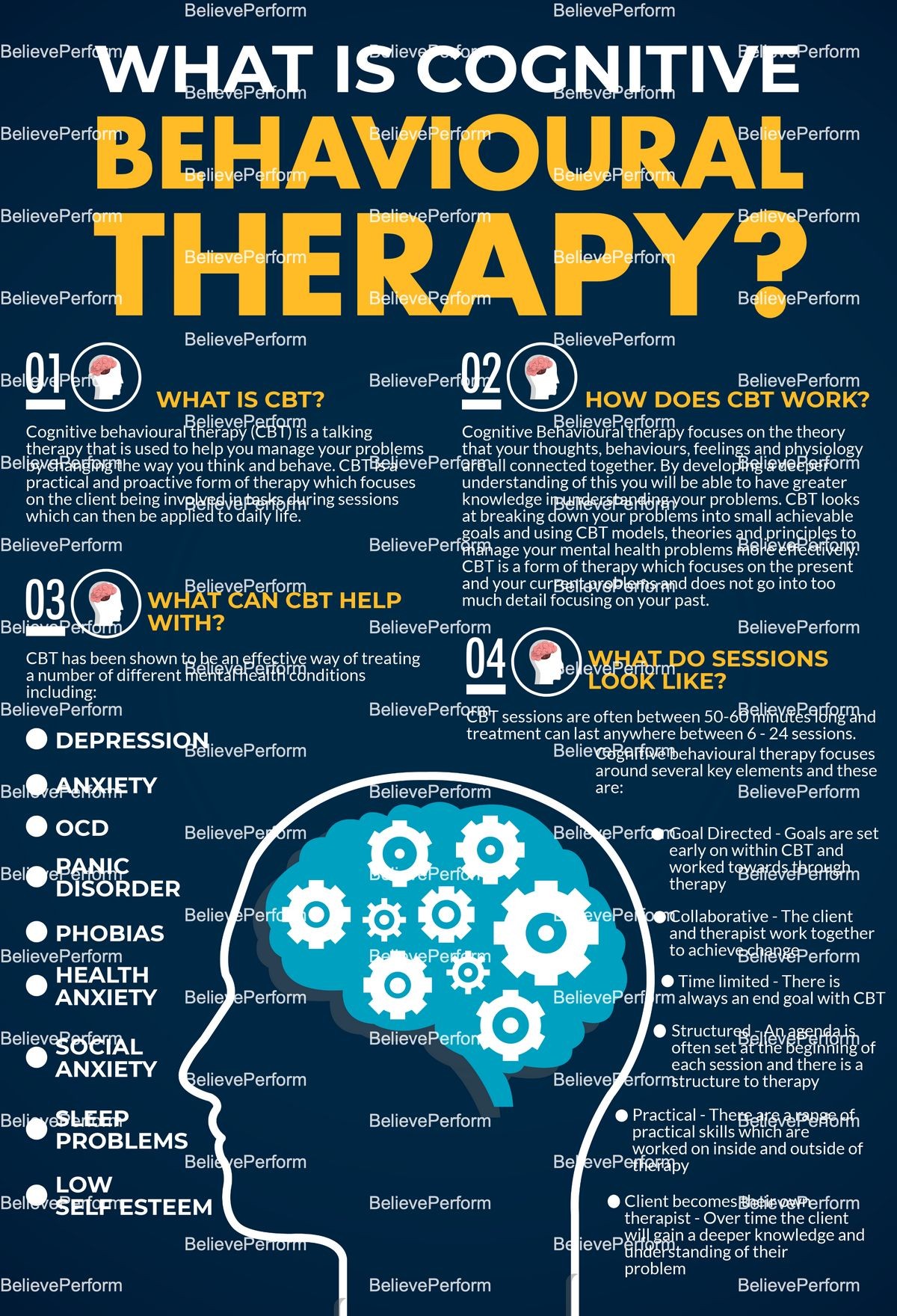
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that helps people manage emotional and behavioral problems by changing their perception of the world and their reactions to it.
CBT focuses on modifying negative emotions, beliefs, and thoughts and uses practical self-help strategies to bring about immediate positive changes. It is suitable for people of all ages and can effectively treat anxiety, depression, developmental disorders such as ADHD and dyslexia, as well as a wide range of mental health disorders and conditions.
How CBT Works
CBT is based on the understanding that thoughts, feelings, physical sensations, and actions are interconnected, and that negative thoughts and feelings can create a vicious cycle. Through CBT, these thoughts and behavior patterns can be changed.
Sessions with a CBT therapist typically last 30-60 minutes and occur on a weekly or biweekly basis. During these sessions, the therapist helps the patient focus on the problem, addresses negative thoughts and behavior patterns, and replaces them with more realistic thoughts that improve mood. CBT focuses on present thoughts and beliefs rather than past issues.
Types of CBT
CBT encompasses a range of cognitive and behavioral techniques and approaches:
Cognitive Therapy
Cognitive therapy helps a person identify and challenge inaccurate or distorted thinking patterns, emotional responses, and behaviors. It provides healthier strategies to change them, also known as cognitive restructuring.
Behavior Therapy
Behavior therapy teaches techniques or skills to alter negative behavior patterns with more positive behaviors.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
DBT addresses and changes negative thoughts and behaviors by incorporating strategies such as emotional regulation and mindfulness.
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT)
REBT involves identifying irrational beliefs and learning to change these thought patterns.
Multimodal Therapy
Multimodal therapy addresses behavior, feeling, imagination, cognition, interpersonal factors, emotions, and biological considerations, viewing them as interconnected modalities.
CBT Techniques
Popular techniques used in CBT include:
- Identifying negative thoughts
- Journaling
- Goal-setting
- Self-talk
- Problem-solving
- Positive activities
- Systematic desensitization
- Situation exposure or role-play
- Homework
Uses of CBT
CBT is effective in treating mental health conditions such as depression, eating disorders, PTSD, anxiety disorders, OCD, and more. It can also help with low self-esteem, general life stress, relationship difficulties, grief, chronic pain, and serious illness.
In addition, CBT is utilized to help individuals cope better with long-term health conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), and fibromyalgia.
Advantages and Limitations of CBT
Advantages of CBT include its effectiveness in cases where medications alone have not worked, shorter treatment periods, structured delivery formats, and the teaching of strategies that can be used beyond therapy.
Limitations of CBT include concerns that it oversimplifies mental health issues, the need for full commitment and cooperation from the individual, the confronting of personal emotions and anxieties, time requirements for sessions and homework, its narrow focus on the individual rather than wider family or systemic problems, and not addressing underlying causes of mental health conditions.