Contents
- 1 Stomach Cancer Survival Rates by Age
- 1.0.1 What is stomach cancer?
- 1.0.2 What are the types of stomach cancer?
- 1.0.3 What are the signs and symptoms of gastric cancer?
- 1.0.4 What are risk factors for stomach cancer?
- 1.0.5 How is stomach cancer diagnosed?
- 1.0.6 What are the stages of stomach cancer?
- 1.0.7 Treatment options for stomach cancer
- 1.0.8 Can stomach cancer be prevented?
- 1.0.9 Subscribe to MedicineNet’s Cancer Report Newsletter
Stomach Cancer Survival Rates by Age
Stomach cancer survival rates decrease with advancing age. Most cases occur between the ages of 65-74, with a median age of 70 for males and 74 for females.
General 5-year survival rates for stomach cancer:
| 15 to 39 | 35 | 33 |
| 40 to 49 | 29 | 31 |
| 50 to 59 | 24 | 26 |
| 60 to 69 | 23 | 25 |
| 70 to 79 | 19 | 22 |
| 80 to 99 | 8 | 9 |
What is stomach cancer?
Stomach cancer occurs when there is an abnormal growth of cells in the stomach due to a mutation in the DNA that causes them to divide and grow uncontrollably.
Most stomach cancers begin in the innermost layer of the stomach. If left untreated, cancer can spread to other parts of the body.
What are the types of stomach cancer?
There are four types of stomach cancer based on the cells from which they arise.
- Adenocarcinoma: the most common type, accounting for more than 90% of all stomach cancers. It occurs in the innermost lining of the stomach (mucosa).
- Lymphoma: accounts for 4% of all stomach cancers, classified as primary and secondary. Primary lymphoma begins in the stomach and spreads to other regions of the body. Secondary lymphoma originates in other regions and then spreads to the stomach.
- GISTs: belong to the sarcoma family and account for only about 1% of stomach cancers. They begin in the connective tissue of the stomach and can be either benign or malignant.
- Carcinoid tumors: account for 3% of all stomach cancers. They originate from hormone-producing cells in the intestine and usually do not spread to other regions.
Other rare types of stomach cancer include squamous cell carcinoma, small cell carcinoma, and leiomyosarcoma.
What are the signs and symptoms of gastric cancer?
Because stomach cancer often grows without causing symptoms, it is rarely discovered in the early stages. When symptoms do appear, they often go unnoticed. Symptoms may include:
- Unintended weight loss
- Abdominal pain or swelling
- Discomfort in the abdomen, often above the navel
- Sense of fullness even after eating a small meal
- Heartburn or indigestion
- Nausea
- Vomiting, with or without blood
- Blood in stools or black tarry stools
- Constipation
- Difficulty swallowing
- Poor appetite
- Fatigue
- Anemia
- Jaundice
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the underarms, belly button, and clavicle
- Persistent burping (belching)
- Fluid buildup in the abdomen
If any of these symptoms occur without relief for a prolonged period, seek medical intervention.
What are risk factors for stomach cancer?
Studies suggest that certain risk factors are linked to stomach cancer. People older than 55 years are more prone to getting stomach cancer. Men are afflicted twice as often as women, and African Americans are more frequently impacted than Caucasians.
- Male gender
- Older age (50 years or older)
- Ethnicity (more common among Hispanic Americans, African Americans, Native Americans, and people of Asian ethnicity)
- Family history of stomach cancer or bowel polyps
- Genetic diseases
- Inflammation of the stomach, such as gastritis or a stomach ulcer
- H. pylori infection
- Epstein-Barr virus infection
- Working in coal, metal, timber, or rubber industries
- Asbestos exposure
- Pernicious anemia
- Compromised immune system (due to conditions like HIV/AIDS)
- History of stomach surgery
- Type A blood
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Obesity
- Consuming certain types of preserved, smoked, or pickled foods
- Diet low in whole foods, particularly fruits and vegetables
Early detection and treatment may result in a better outcome regardless of the cause of stomach cancer.
What Is Polycythemia Vera?
How is stomach cancer diagnosed?
Diagnostic tests are used to confirm the presence of cancer and determine the stage, which can help determine treatment. The following tests are often used to diagnose stomach cancer:
- Physical examination
- Blood tests
- Fecal occult blood test
- Imaging tests like ultrasound and computed tomography scan
- Endoscopy
- Endoscopic ultrasound
- Biopsy of the tumor
- Exploratory surgery
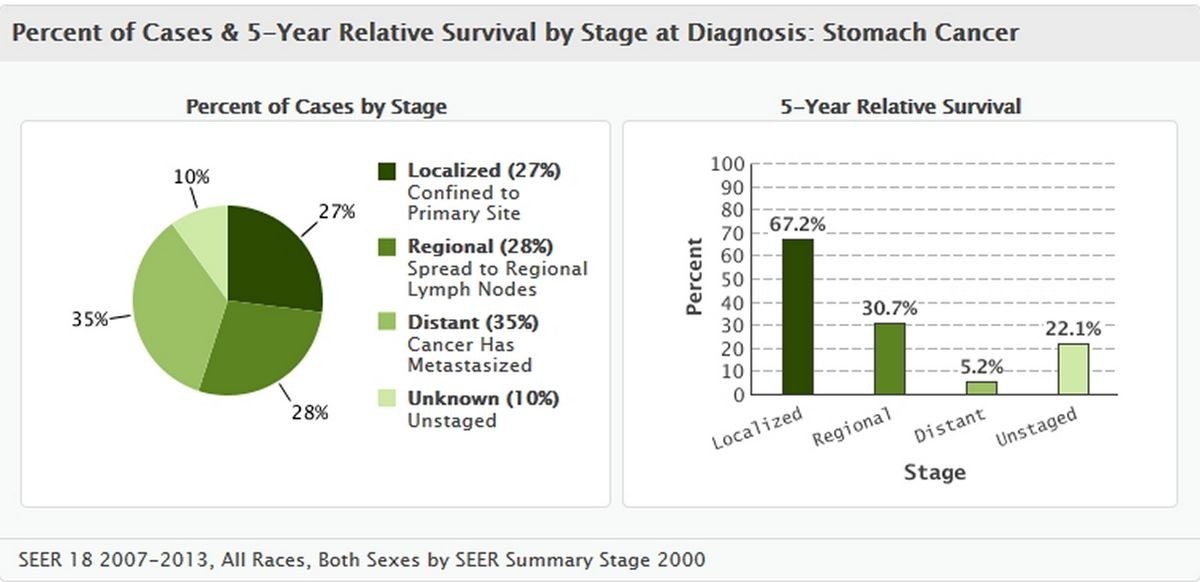
What are the stages of stomach cancer?
Staging is determined by the extent of cancer in the body, where it was found, whether it has spread, and where it has spread to.
The stage of the cancer helps determine the response to therapy and the likelihood of recurrence.
- Stage I:
- Stage IA: Cancer may have migrated to the submucosa of the stomach wall.
- Cancer may have spread to the submucosa and 1-2 lymph nodes, or it may have migrated to the muscular layer of the stomach wall.
- Tumor has spread to 7-15 lymph nodes or other organs from the inner lining of the stomach.
- Tumor has migrated to the stomach wall’s outer muscle layer and 1-6 lymph nodes.
- Tumor has migrated through the stomach wall but not to any lymph nodes or other organs.
- Stage IIIA:
- Tumor has migrated to the stomach’s outer muscular layer and 7-15 lymph nodes, but not to other organs.
- Tumor has migrated through the stomach wall and 1-6 lymph nodes, but not to other organs.
- Tumor has migrated to neighboring organs, but not to lymph nodes or distant organs.
- Tumor has spread to 7-15 lymph nodes after growing through the stomach wall.
- Cancer has spread to other organs like the liver, peritoneum, lungs, and brain.
Treatment options for stomach cancer
Treatment options vary depending on factors like the stage of cancer, general health, and potential adverse effects of medications.
1. Surgery
- Endoscopic mucosal resection: Used for early-stage stomach cancer that has not spread.
- Subtotal or partial gastrectomy: Surgical removal of cancerous tumors in the stomach, nearby lymph nodes, and organs.
- Total gastrectomy: Surgical removal of the entire stomach, along with lymph nodes and adjacent organs.
2. Chemotherapy
- Drugs are used to kill or slow the growth of cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy may be combined with radiation or surgery for enhanced effectiveness.
3. Radiation
- High-energy X-rays or protons are used to destroy cancer cells.
- It can be combined with chemotherapeutic drugs for enhanced effectiveness.
4. Targeted therapy
- Medications specifically target and destroy cancer cells.
5. Immunotherapy
Drugs are given to strengthen the immune system, enabling it to target and eliminate stomach cancer cells.
6. Clinical trials
- Clinical trials allow patients to receive novel drugs being researched for stomach cancer treatment.
7. Supportive care
- Oncology teams provide supportive care to improve patients’ quality of life with the help of counselors, nurses, nutritionists, and social service experts.
Can stomach cancer be prevented?
Prevention measures may include:
- Eating at least 5 servings of fresh fruits and vegetables each day
- Including whole grains and legumes in your diet
- Avoiding consumption of salted, pickled, and smoked foods
- Limiting consumption of red meat
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Seeking prompt medical consultation if you notice symptoms
Subscribe to MedicineNet’s Cancer Report Newsletter
By clicking "Submit," I agree to the MedicineNet Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy and to receive emails from MedicineNet. I understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet subscriptions at any time.
By clicking "Submit," I agree to the MedicineNet Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy and to receive emails from MedicineNet. I understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet subscriptions at any time.