Contents
Stem Cells
Stem cells are cells with the potential to develop into different cell types. They are "unspecialized" cells that can divide and become specialized cells such as liver cells, muscle cells, blood cells, and others.
Stem cells are referred to as "undifferentiated" cells because they have not committed to a specific path of development. Changing into a specific cell type is called differentiation. Stem cells divide regularly in some parts of the body to renew and repair tissue, such as bone marrow and gastrointestinal tract.
The best example of a stem cell is the zygote, which is formed by the union of a sperm and an ovum. The zygote becomes an embryo that rapidly multiplies and develops into an organism composed of specialized cells.
- A zygote is a single cell that becomes an embryo, which ultimately grows into a sophisticated organism.
- That organism consists of billions of cells with diverse functions.
- All of these specialized cells are descendants of the original zygote, a stem cell with the potential to develop into any type of cell.
The process by which stem cells become specialized cells is complex and involves gene expression regulation. Research is ongoing to understand these molecular events and controls.
Why are stem cells important?
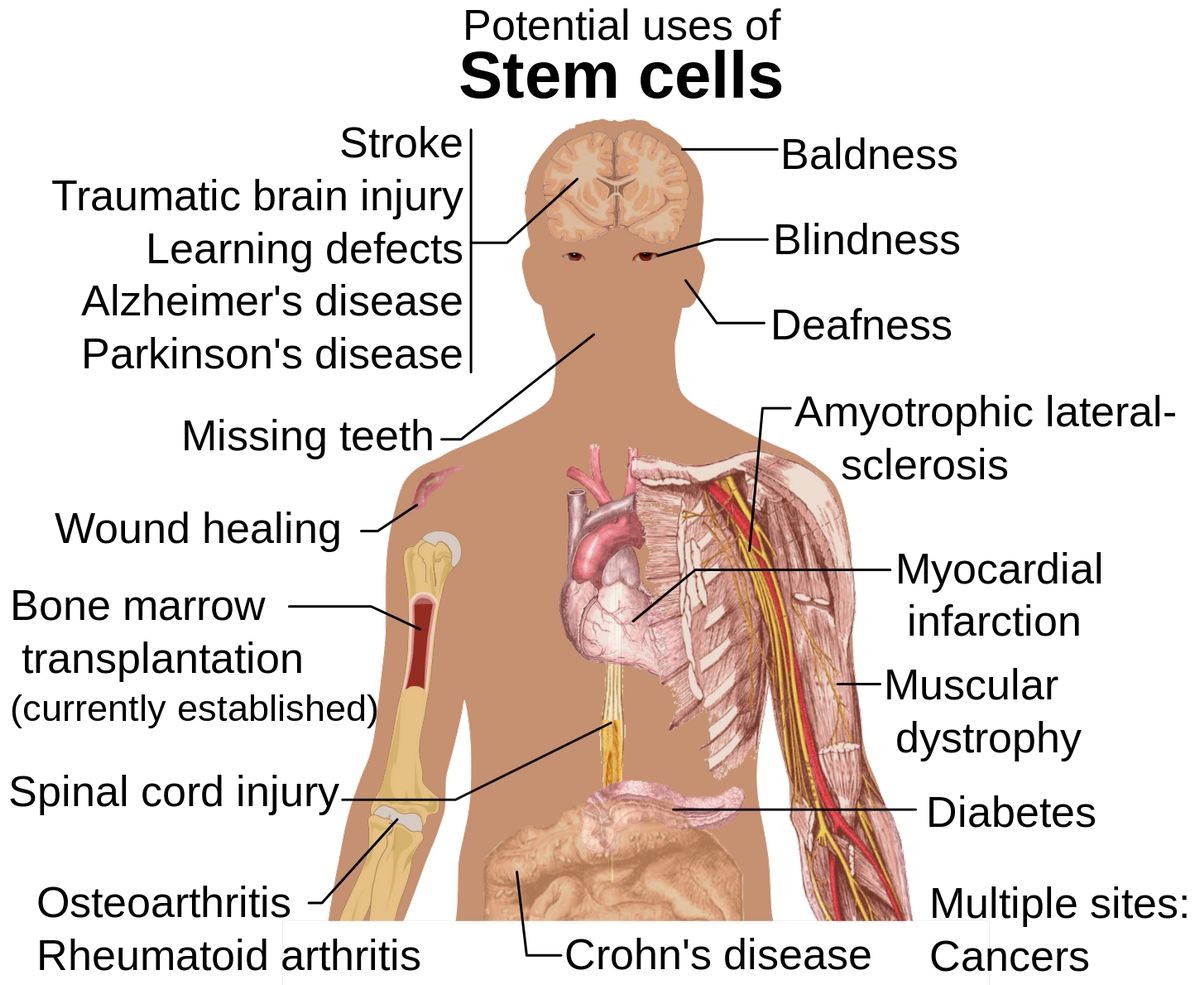
Stem cells are significant in medicine because they can regenerate and repair damaged tissue. Current therapies, like bone marrow transplantation, already make use of stem cells for tissue regeneration.
Other therapies under investigation involve transplanting stem cells into damaged body parts and directing them to grow into healthy tissue.
Where do they get stem cells from?
Stem cells are obtained from various sources depending on the type needed and the disease being treated.
Common sources of stem cells include:
- Embryonic stem cells
- Fetal stem cells
- Adult stem cells
- Peripheral stem cells
- Perinatal stem cells
- Induced pluripotent stem cells
Embryonic stem cells
During early embryonic development, cells are undifferentiated and have the potential to become any tissue in the body. For example, cells from one section of an embryo can become blood, muscle, nerve, or liver cells.
Fetal stem cells
The fetal stage contains pluripotent stem cells that develop into different body tissues.
Adult stem cells
Adult stem cells are present in small numbers and are tissue-specific. They can only develop into certain types of cells.
Peripheral blood stem cells
Some stem cells are present in the bloodstream and can be isolated from a blood sample. They can develop into various blood and immune system cells.
Perinatal stem cells
Umbilical cord blood and amniotic fluid contain stem cells that can differentiate into specific cell types. Umbilical cord blood is often stored for potential future use in stem cell therapy.
Induced pluripotent stem cells
Induced pluripotent stem cells are adult cells genetically converted into an embryonic stem cell-like state. They can differentiate into multiple fetal cell types and aid in disease research and drug treatment.
Why is there controversy surrounding the use of stem cells?
Embryonic stem cells and embryonic stem cell lines have ethical considerations because they are derived from human embryos created through IVF or cloning technologies.
What stem cell therapies are currently available?
Stem cell therapy is primarily used in bone marrow transplantation to treat blood-related cancers and disorders. Stem cells from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood are transplanted to regenerate the patient’s bone marrow and produce healthy blood cells.
Is stem cell therapy FDA approved?
The FDA has approved some stem cell therapies for specific medical conditions. However, many therapies are still experimental and not fully tested. The FDA takes action against clinics offering unapproved therapies.
One FDA-approved stem cell therapy is hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for bone marrow and blood-related diseases.


