Contents
vasopressin
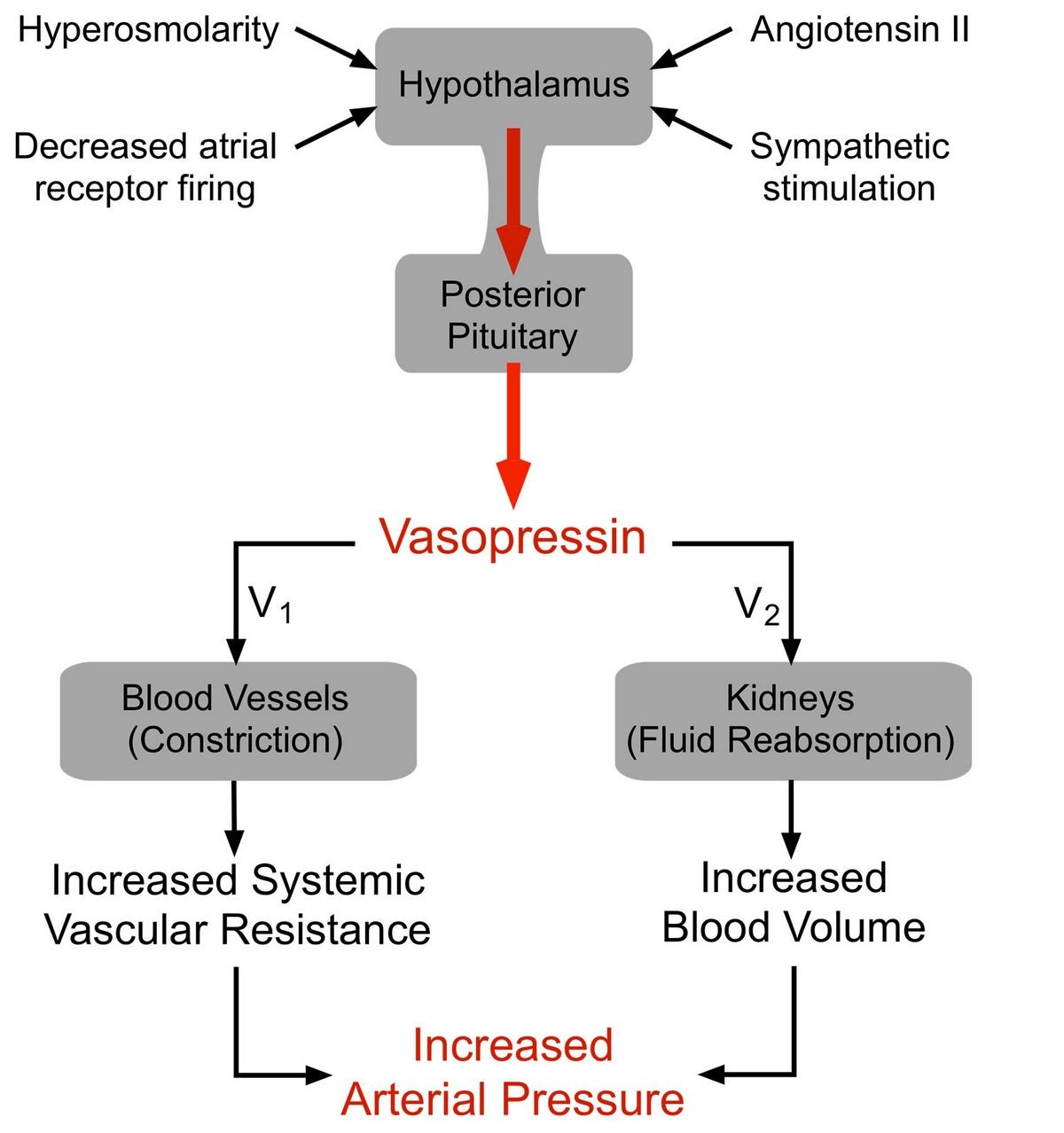
Vasopressin, also known as arginine vasopressin or antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is a natural substance synthesized in the hypothalamus in the brain. Vasopressin regulates fluid and electrolyte balance, blood pressure, sodium levels, and kidney function. It is released when blood’s water content drops or if blood volume is reduced. Vasopressin increases water reabsorption in the kidneys.
Synthetically produced vasopressin is used to increase blood pressure in adults with severely low blood pressure from vasodilatory shock. Vasopressin increases vascular resistance, arterial blood pressure, and water reabsorption. It also promotes peristalsis in the gastrointestinal tract.
Vasopressin is typically administered with intravenous fluids and norepinephrine to restore normal blood pressure in adults with vasodilatory shock. It reduces the requirement of norepinephrine and tends to lower heart rate and cardiac output.
Off-label uses of vasopressin include diabetes insipidus, abdominal distention after certain surgeries, abdominal x-ray, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and hormone replacement therapy in brain-dead donors.
Warnings
- Do not use vasopressin in patients with known hypersensitivity to 8-L-arginine vasopressin, any of the components in vasopressin formulation, or chlorobutanol (multiple dose vial only, single dose vial does not contain chlorobutanol).
- Reversible diabetes insipidus may occur after discontinuation of vasopressin. Monitor patient’s urine output, fluid and electrolyte balance, and consider readministration of vasopressin or administration of desmopressin.
- Use vasopressin with caution in patients with cardiovascular disease.
- Monitor for symptoms of water intoxication and promptly treat to prevent coma and seizures.
- Avoid extravasation during infusion to prevent tissue death.
- Continue vasopressin infusion for 12-24 hours after gastrointestinal bleeding has stopped and taper the dosage over 24-48 hours.
- Administer continuous infusion of vasopressin via controlled infusion device.
- Use vasopressin with caution in patients with kidney disease, migraine, seizures, asthma, or vascular disease.
What are the side effects of vasopressin?
Common side effects of vasopressin include hemorrhagic shock, decrease in platelets, intractable bleeding, right heart failure, rapid irregular rhythm of atria (atrial fibrillation), slow heart rate (bradycardia), reduced blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardial ischemia), lower limb ischemia, abdominal (mesenteric) ischemia, ischemic lesions in the skin, increased bilirubin levels, acute kidney insufficiency, low sodium levels (hyponatremia), abdominal cramps, diarrhea, nausea, bronchial constriction, paleness around the mouth (circumoral pallor), chest pain (angina), pounding in the head, sweating, tremor, vertigo, uterine contraction, allergic reaction, and reversible diabetes insipidus.
Call your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms or serious side effects while using this drug:
- Fast or pounding heartbeats, fluttering in your chest, shortness of breath, and sudden dizziness;
- Severe headache, confusion, slurred speech, severe weakness, vomiting, loss of coordination, feeling unsteady;
- Severe nervous system reaction with very stiff muscles, high fever, sweating, confusion, fast or uneven heartbeats, tremors, and feeling like you might pass out; or
- Serious eye symptoms include blurred vision, tunnel vision, eye pain or swelling, or seeing halos around lights.
This is not a complete list of all side effects or adverse reactions that may occur from the use of this drug. Call your doctor for medical advice about serious side effects or adverse reactions. You may also report side effects or health problems to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
What are the dosages of vasopressin?
Injection Solution for Dilution
- 20 units/mL (3-mL single-dose vial; 10-mL multidose vial); further dilution required /100mL
Injection Solution, Ready-To-Use
- 20 units/100mL (0.2 units/mL)
- 40 units/100mL (0.4 units/mL)
- 60 units/100mL (0.6 units/mL)
Adult:
Vasodilatory Shock
- Indicated to increase blood pressure in adults with vasodilatory shock who remain hypotensive despite fluids and catecholamines
- Titrate to lowest dose compatible with clinically acceptable response
- Postcardiotomy shock (initial dose): 0.03 units/minute intravenous (IV)
- Septic shock (initial dose): 0.01 unit/minute IV
- Titrate up by 0.005 unit/minute at 10- to 15-minute intervals until target blood pressure reached
- Data are limited for doses greater than 0.1 unit/minute for postcardiotomy shock and 0.07 unit/minute for septic shock; adverse reactions expected to increase with higher doses
- Taper vasopressin injection by 0.005 units/minute every hour after target blood pressure has been maintained for 8 hours without use of catecholamines
- No dosage adjustment provided for hepatic or renal impairment
Abdominal Distention (Off-label)
- 5 units intramuscular (IM) initially; repeated every 3 to 4 hours as needed; may be increased to 10 units
Diabetes Insipidus (Off-label)
- 5-10 units intramuscular/subcutaneous (IM/SC) every 8 to 12 hours
- Titrate dose based on serum sodium, serum osmolality, fluid balance, and urine output
Abdominal Roentgenography (Off-label)
- 10 units (0.5mL) IM/SC 2 hours before procedure, then 10 units IM 30 minutes before procedure
- May give enema prior to first dose of vasopressin
Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage (Off-label)
- 0.2-0.4 unit/min IV initially; may be increased to 0.8 unit/min IV as needed
Pediatric:
- Safety and efficacy not established.
Overdose
- Vasopressin overdose may cause constriction of various blood vessels and gastrointestinal symptoms. It may also cause muscle cell breakdown and life-threatening ventricular heart rhythm disorders.
- Direct effects of vasopressin usually resolve within minutes of discontinuation. Residual symptoms may be treated with supportive and symptomatic care.
What drugs interact with vasopressin?
Inform your doctor of all medications you are currently taking, who can advise you on any possible drug interactions. Never begin taking, suddenly discontinue, or change the dosage of any medication without your doctor’s recommendation.
- Vasopressin has no known severe, serious, or moderate interactions with other drugs.
- Vasopressin has mild interactions with at least 24 different drugs.
The drug interactions listed above are not all of the possible interactions or adverse effects. For more information on drug interactions, visit the RxList Drug Interaction Checker.
Always tell your doctor, pharmacist, or health care provider of all medications you use and keep a list of the information. Check with your doctor or health care provider if you have any questions about the medication.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- There are no available data on the effects of maternal use of vasopressin during pregnancy. It is not known if the drug can cause birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
- Vasopressin doses may need to be increased during the second and third trimesters.
- Use only when clearly needed in pregnant women.
- No information on vasopressin effects on human or animal milk production, or the effects on the breastfed infant.
By clicking "Submit," I agree to the MedicineNet Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy. I also agree to receive emails from MedicineNet and I understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet subscriptions at any time.
Summary
Synthetically produced vasopressin is used to increase blood pressure in adults with severely low blood pressure from vasodilatory shock. Common side effects of vasopressin include hemorrhagic shock, decrease in platelets, intractable bleeding, right heart failure, rapid irregular rhythm of atria, slow heart rate, reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, lower limb ischemia, abdominal ischemia, ischemic lesions in the skin, increased bilirubin levels, acute kidney insufficiency, low sodium levels, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, nausea, bronchial constriction, and others. Consult your doctor if pregnant or breastfeeding.
Synthetically produced vasopressin is used to increase blood pressure in adults with severely low blood pressure from vasodilatory shock. Common side effects of vasopressin include hemorrhagic shock, decrease in platelets, intractable bleeding, right heart failure, rapid irregular rhythm of atria, slow heart rate, reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, lower limb ischemia, abdominal ischemia, ischemic lesions in the skin, increased bilirubin levels, acute kidney insufficiency, low sodium levels, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, nausea, bronchial constriction, and others. Consult your doctor if pregnant or breastfeeding.