Contents
Side Effects of Precose (acarbose)
Carbohydrates are digested by enzymes in the intestine into smaller sugars, which increase blood sugar levels.
Carbohydrate digestion requires the pancreas to release alpha-amylase enzymes that digest carbohydrates into smaller oligosaccharides.
The cells lining the small intestine release alpha-glucosidase enzymes that further digest oligosaccharides into smaller sugars that can be absorbed.
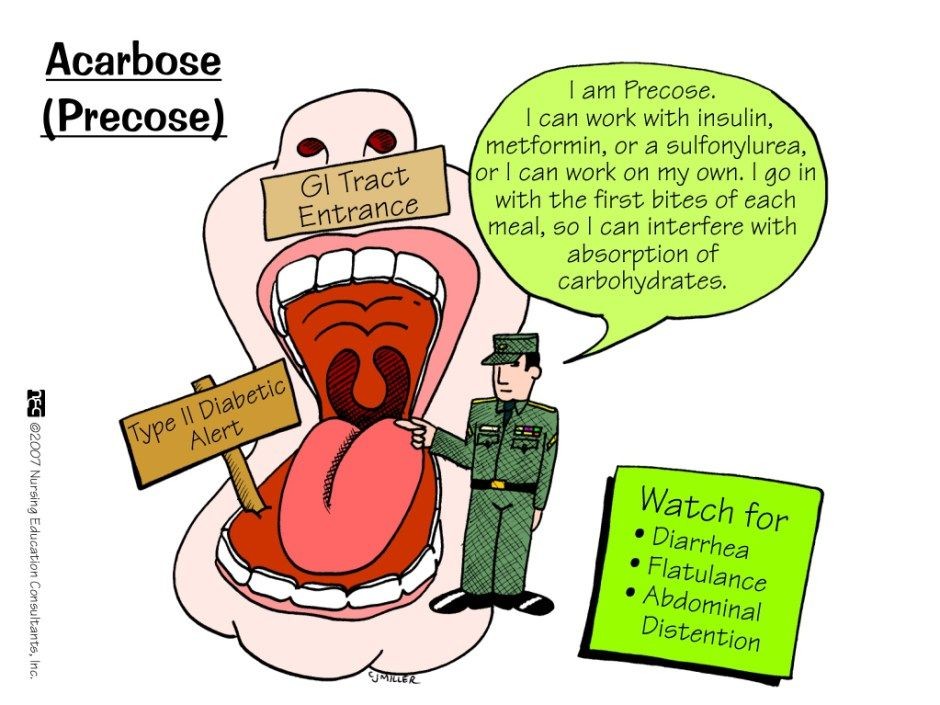
Precose is a man-made oligosaccharide designed to slow down the actions of alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase enzymes, thereby slowing the appearance of sugar in the blood after a meal.
Common side effects of Precose include
- abdominal pain,
- diarrhea,
- gas (flatulence), and
- increased liver enzymes.
Serious side effects of Precose include
- decreases in hematocrit, calcium or vitamin B6 levels;
- liver failure,
- yellowing skin and eyes (jaundice),
- hepatitis,
- low blood platelets (thrombocytopenia),
- severe skin reactions (rash, redness, and hives),
- pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis infection, and rarely,
- severe gastrointestinal side effects that may progress to intestinal obstruction caused by paralysis of the intestinal muscles (paralytic ileus).
Drug interactions of Precose include digoxin absorption, bcause it may decrease digoxin blood levels and its effect.
- Adding insulin or a sulfonylurea to Precose therapy may lower blood glucose more than acarbose alone, increasing the risk of hypoglycemia when combined.
- Charcoal may absorb Precose and digestive enzyme preparations such as amylase or pancreatin may breakdown acarbose and should not be administered with this diabetes drug.
There are no studies of Precose treatment during pregnancy in humans. Insulin therapy is recommended in pregnancy.
Precose is excreted in the milk of lactating animals, but no human studies have been conducted. Precose use is not recommended for women who are breastfeeding.
What are the important side effects of Precose (acarbose)?
The most common side effects include:
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Flatulence (gas)
- An increase in liver enzymes
There is a rare possibility that these gastrointestinal side effects may become severe and progress to intestinal obstruction caused by paralysis of the intestinal muscles (paralytic ileus).
Possible serious, but rare side effects include:
- Decreases in hematocrit, calcium or vitamin B6 levels
- Liver failure
- Jaundice
- Hepatitis
- Ileus
- A reduction in the number of platelets (thrombocytopenia)
- Severe skin reactions (rash, erythema, exantherma, and hives)
- Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis infection
Precose (acarbose) side effects list for healthcare professionals
Digestive Tract
Gastrointestinal symptoms are the most common reactions to Precose. In U.S. placebo-controlled trials, the incidences of abdominal pain, diarrhea, and flatulence were 19%, 31%, and 74% respectively in 1255 patients treated with Precose 50–300 mg t.i.d., whereas the corresponding incidences were 9%, 12%, and 29% in 999 placebo-treated patients.
In a one-year safety study, during which patients kept diaries of gastrointestinal symptoms, abdominal pain and diarrhea tended to return to pretreatment levels over time, and the frequency and intensity of flatulence tended to abate with time.
The increased gastrointestinal tract symptoms in patients treated with Precose are a manifestation of the mechanism of action and are related to the presence of undigested carbohydrate in the lower GI tract.
If the prescribed diet is not observed, the intestinal side effects may be intensified. If strongly distressing symptoms develop in spite of adherence to the diabetic diet prescribed, the doctor must be consulted and the dose temporarily or permanently reduced.
Elevated Serum Transaminase Levels
See prescribing information for further details on precautions.
Other Abnormal Laboratory Findings
Small reductions in hematocrit occurred more often in Precose-treated patients than in placebo-treated patients but were not associated with reductions in hemoglobin.
Low serum calcium and low plasma vitamin B6 levels were associated with Precose therapy but are thought to be either spurious or of no clinical significance.
Postmarketing Adverse Event Reports
Additional adverse events reported from worldwide postmarketing experience include
- fulminant hepatitis with fatal outcome,
- hypersensitive skin reactions (for example rash, erythema, exanthema and uticaria),
- edema,
- ileus/subileus,
- jaundice and/or hepatitis and associated liver damage,
- thrombocytopenia, and
- pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis.
Pneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis
There have been rare postmarketing reports of pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis associated with the use of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, including Precose.
Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis may present with symptoms of
- diarrhea,
- mucus discharge,
- rectal bleeding, and
- constipation.
Complications may include
- pneumoperitoneum,
- volvulus,
- intestinal obstruction,
- intussusception,
- intestinal hemorrhage, and
- intestinal perforation.
If pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis is suspected, discontinue Precose and perform the appropriate diagnostic imaging.
What drugs interact with Precose (acarbose)?
Certain drugs tend to produce hyperglycemia and may lead to loss of blood glucose control. These drugs include thiazides and other
- diuretics,
- corticosteroids,
- phenothiazines,
- thyroid products,
- estrogens,
- oral contraceptives,
- phenytoin,
- nicotinic acid,
- sympathomimetics,
- calcium channel-blocking drugs, and
- isoniazid.
When such drugs are administered to a patient receiving Precose, the patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control. When such drugs are withdrawn from patients receiving Precose in combination with sulfonylureas or insulin, patients should be observed closely for any evidence of hypoglycemia.
Patients Receiving Sulfonylureas or Insulin: Sulfonylurea agents or insulin may cause hypoglycemia. Precose given in combination with a sulfonylurea or insulin may cause a further lowering of blood glucose and may increase the potential for hypoglycemia.
If hypoglycemia occurs, appropriate adjustments in the dosage of these agents should be made.
Very rarely, individual cases of hypoglycemic shock have been reported in patients receiving Precose therapy in combination with sulfonylureas and/or insulin.
Intestinal adsorbents and digestive enzyme preparations containing carbohydrate-splitting enzymes may reduce the effect of Precose and should not be taken concomitantly.
Precose has been shown to change the bioavailability of digoxin when they are coadministered, which may require digoxin dose adjustment.
Summary
Precose (acarbose) is an oral alpha-glucosidase inhibitor used to control blood glucose levels in people with type 2 diabetes. Common side effects include abdominal pain, diarrhea, gas, and increased liver enzymes. Precose is not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding.


