Contents
Side Effects of Catapres (clonidine)
Catapres (clonidine) is a centrally acting alpha-agonist hypotensive agent used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). It may be used alone or combined with other drugs for hypertension treatment.
Catapres is also used off-label to treat alcohol withdrawal, smoking cessation (nicotine withdrawal), restless leg syndrome, Tourette’s syndrome, opioid withdrawal, diabetes-associated diarrhea, diabetic neuropathy (nerve damage), hot flashes associated with menopause, and severe cancer-related pain management.
It acts by stimulating receptors on brain nerves to reduce message transmission to other parts of the body. This slows the heart rate and lowers blood pressure.
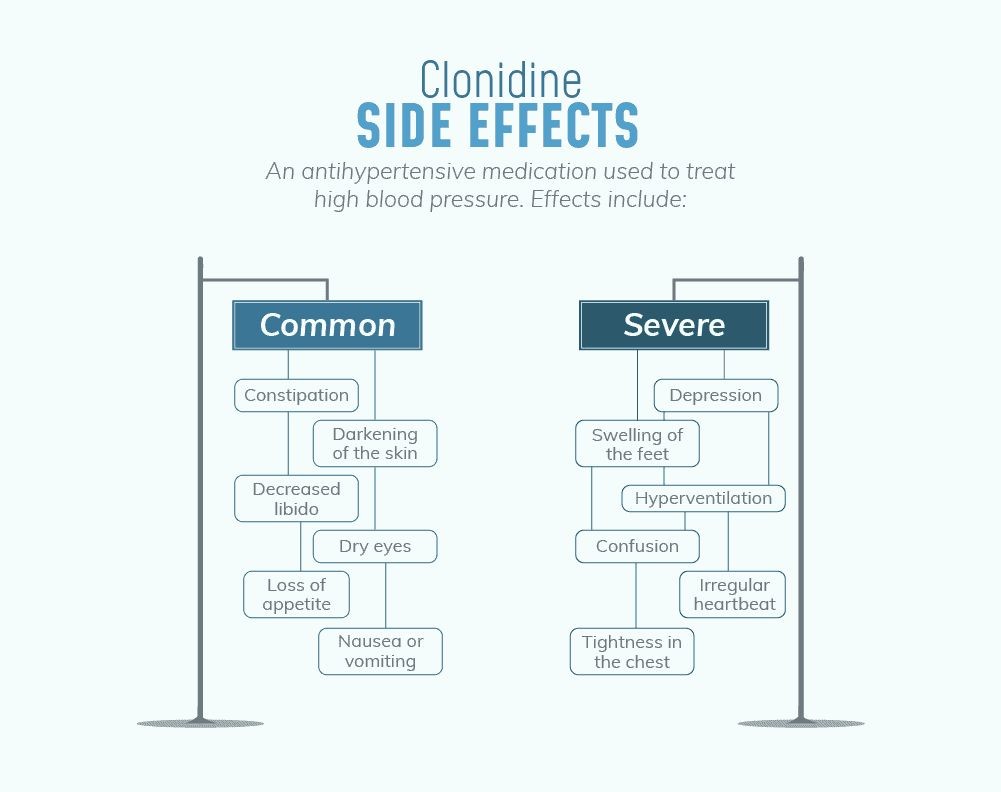
Common side effects of Catapres:
- tiredness
- lethargy
- fatigue
- drowsiness
- weakness
- constipation
- dry mouth
- headache
- dizziness
- skin redness
- itching
- darkening of skin
- impotence
- decreased sexual desire
- ejaculatory dysfunction
Serious side effects of Catapres:
- severe rebound high blood pressure (more likely if Catapres is stopped suddenly; symptoms may include increased salivation, nervousness, headache, heart palpitations, agitation, anxiety, sweating, nausea, muscle pain, and abdominal pain)
- severe low blood pressure
- slow heart rate
- withdrawal symptoms
- depression
- angioedema
- severe allergic reactions
- fainting
- abnormal heart conduction
Drug interactions of Catapres:
- sedating medications (e.g., narcotic pain relievers, barbiturates, sedatives, and ethanol) can have increased sedating effects when combined with Catapres
- tricyclic antidepressants can block the blood pressure lowering effects of Catapres; caution should be used with other heart rate lowering medications
- a combination of Catapres and verapamil can cause abnormal heart rhythms
- catapres may increase blood concentrations of cyclosporine, resulting in kidney damage
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), cocaine, and certain other drugs can reverse the blood pressure lowering effects of Catapres
There is limited information about the use of Catapres during pregnancy and breastfeeding, therefore consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
What are the important side effects of Catapres (clonidine)?
The most common side effects:
Other side effects:
- skin redness
- itching
- impotence
- darkening of skin
- decreased sexual desire
- ejaculatory dysfunction
Possible serious side effects:
- severe rebound high blood pressure
- severe low blood pressure
- slow heart rate
- withdrawal symptoms
- depression
- angioedema
- severe allergic reactions
- slow heart rate
- fainting
- abnormal heart conduction
Withdrawal from clonidine may cause severe rebound hypertension, especially if stopped suddenly. Symptoms may include increased salivation, nervousness, headache, heart palpitations, agitation, anxiety, sweating, nausea, muscle pain, and abdominal pain. Gradual dose reduction can prevent these symptoms.
Catapres (clonidine) side effects list for healthcare professionals
Most adverse effects are mild and tend to diminish with continued therapy. The most frequent (which appear to be dose-related) are dry mouth (40%), drowsiness (33%), dizziness (16%), constipation (10%), and sedation (10%).
Less frequent adverse experiences have also been reported, but a causal relationship has not been established. These include fatigue, headache, weakness, withdrawal syndrome, a weak positive Coombs’ test, increased sensitivity to alcohol, bradycardia, congestive heart failure, electrocardiographic abnormalities, orthostatic symptoms, palpitations, Raynaud’s phenomenon, syncope, tachycardia, agitation, anxiety, delirium, delusional perception, hallucinations, insomnia, mental depression, nervousness, other behavioral changes, paresthesia, restlessness, sleep disorder, vivid dreams or nightmares, alopecia, angioneurotic edema, hives, pruritus, rash, urticaria, abdominal pain, anorexia, hepatitis, malaise, mild transient abnormalities in liver function tests, nausea, parotitis, pseudo-obstruction, salivary gland pain, vomiting, decreased sexual activity, difficulty in micturition, erectile dysfunction, loss of libido, nocturia, urinary retention, thrombocytopenia, gynecomastia, transient elevation of blood glucose or serum creatine phosphokinase, weight gain, leg cramps, muscle or joint pain, dryness of the nasal mucosa, accommodation disorder, blurred vision, burning of the eyes, decreased lacrimation, and dryness of the eyes.
What drugs interact with Catapres (clonidine)?
- Clonidine may potentiate the CNS-depressive effects of alcohol, barbiturates, or other sedating drugs.
- Clonidine dose increase may be necessary when taken with tricyclic antidepressants.
- Orthostatic regulation disturbances may occur with neuroleptics and clonidine.
- Heart rate should be monitored when clonidine is taken with agents affecting sinus node or AV nodal conduction.
- Sinus bradycardia has been reported with clonidine and diltiazem or verapamil.
- Corneal lesions in rats are enhanced by clonidine in combination with amitriptyline.
- High doses of clonidine and haloperidol may increase arrhythmogenic potential.
- There is no established relationship between clonidine oral tablets and the drugs listed.
Summary
Catapres (clonidine) is a centrally acting alpha-agonist hypotensive agent used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). It may be used alone or in combination with other drugs for hypertension treatment. Common side effects of Catapres include tiredness, lethargy, fatigue, drowsiness, weakness, constipation, dry mouth, headache, dizziness, skin redness, itching, darkening of skin, impotence, decreased sexual desire, and ejaculatory dysfunction. Limited information is available about Catapres use during pregnancy and breastfeeding, so consult your doctor before breastfeeding.