Contents
selexipag
Selexipag is a medication used to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), a condition of high blood pressure in the arteries that carry oxygen-depleted blood from the heart to the lungs. It belongs to a class of medications known as prostacyclin agonists that reduce pulmonary hypertension by dilating the blood vessels. Selexipag is taken as oral tablets or administered as intravenous injections to delay disease progression and reduce the risk of hospitalization in PAH patients.
Prostacyclin is a type of prostaglandin known as prostaglandin I2 (PGI2), a natural substance produced by the endothelial cells lining the blood vessels. It helps maintain normal blood pressure and smooth blood flow. Prostaglandins are hormone-like substances with multiple functions in the body, including inflammation mediation, pain relief, and contraction of smooth muscles around organs.
Prostaglandins work by stimulate prostanoid receptors on cell surfaces. Prostacyclin stimulates IP receptors specifically, inhibiting proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and platelet aggregation. This helps maintain normal blood pressure and prevent blood clotting.
In PAH patients, there is a decrease in prostacyclin and prostacyclin synthase, the enzyme that produces prostacyclin, in the lungs. Selexipag selectively stimulates IP receptors and produces similar effects to prostacyclin, reducing pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Warnings
- Avoid using selexipag if you are hypersensitive to any component of the medication.
- Avoid concomitant use of selexipag with strong CYP2C8 inhibitor drugs like gemfibrozil. This can increase exposure to selexipag and its metabolite.
- Use caution when combining selexipag with inducers of CYP2C8 and UGT 1A3 and 2B7 enzymes, such as rifampin, as it can reduce the bioavailability of selexipag.
- Monitor patients for signs of pulmonary edema (fluid in the lungs) and evaluate for pulmonary veno-occlusive disease if needed. Discontinue selexipag if confirmed.
Side Effects
Common side effects of selexipag include:
- Headache
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Reduced appetite
- Jaw pain
- Muscle pain
- Limb pain
- Joint pain
- Rash
- Flushing
- Anemia
- Drop in hemoglobin levels
- Infusion site reactions
Seek medical help immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms or serious side effects:
- Serious heart symptoms such as fast or pounding heartbeats, chest fluttering, shortness of breath, and sudden dizziness
- Severe headache, confusion, slurred speech, severe weakness, vomiting, loss of coordination, feeling unsteady
- Severe nervous system reaction with very stiff muscles, high fever, sweating, confusion, fast or uneven heartbeats, tremors, and feeling like you might faint
- Serious eye symptoms like blurred vision, tunnel vision, eye pain or swelling, or seeing halos around lights
This is not a complete list of side effects or adverse reactions. Contact your doctor or report side effects to the FDA.
Dosages
Tablet
- 200 mcg
- 400 mcg
- 600 mcg
- 800 mcg
- 1000 mcg
- 1200 mcg
- 1400 mcg
- 1600 mcg
Injection, lyophilized powder for reconstitution
- 1800 mcg/vial
- Reconstituted concentration of each vial: 225 mcg/mL
Adult Dosage for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
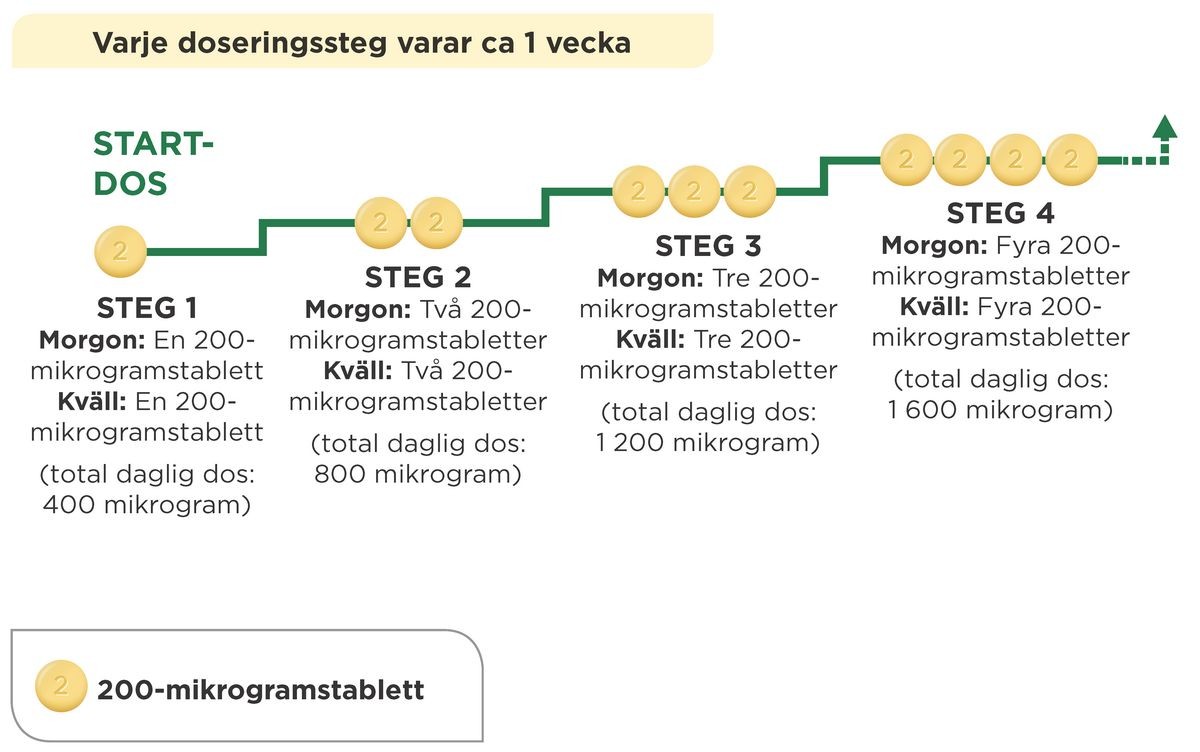
- Start with 200 mcg orally twice daily
- Increase by 200 mcg twice daily, at weekly intervals, to highest tolerated dose (usually not exceeding 1600 mcg twice daily)
- If dose is not tolerated, reduce to previous tolerated dose
Oral to intravenous (IV) conversion:
- Use in patients temporarily unable to take orally
- Current oral dose 200 mg twice daily: Administer 225 mg IV twice daily
- Current oral dose 400 mg twice daily: Administer 450 mg IV twice daily
- Current oral dose 600 mg twice daily: Administer 675 mg IV twice daily
- Current oral dose 800 mg twice daily: Administer 900 mg IV twice daily
- Current oral dose 1000 mg twice daily: Administer 1125 mg IV twice daily
- Current oral dose 1200 mg twice daily: Administer 1350 mg IV twice daily
- Current oral dose 1400 mg twice daily: Administer 1575 mg IV twice daily
- Current oral dose 1600 mg twice daily: Administer 1800 mg IV twice daily
Dosage Modifications
- No dosage adjustment required for eGFR above 15 mL/minute/1.73 m2
- No clinical experience for eGFR below 15 mL/minute/1.73 m2 or patients undergoing dialysis
- Mild (Child-Pugh A): No dosage adjustment required
- Moderate (Child-Pugh B): Start with 200 mcg once daily; increase incrementally at weekly intervals, as tolerated
- Severe (Child-Pugh C): Avoid use
- Reduce selexipag dose to once daily if coadministered with moderate CYP2C8 inhibitors (e.g., clopidogrel, deferasirox, teriflunomide)
- Revert to twice daily dosing when moderate CYP2C8 inhibitor is discontinued
- Increase selexipag dose if coadministerd with rifampin (up to 2-fold)
Dosage Considerations
- Effectiveness was established in a long-term study in patients with PAH with WHO Functional Class II-III symptoms
- Patients had idiopathic and heritable PAH (58%), PAH associated with connective-tissue disease (29%), or PAH associated with congenital heart disease with repaired shunts (10%)
Pediatric Safety and Efficacy
- Not established
Overdose
There is limited experience with selexipag overdose. Mild, transient nausea was the only reported symptom with overdoses of up to 3200 mcg. Care for selexipag overdose involves symptomatic and supportive measures.
Drug Interactions
Inform your doctor of all medications you are currently taking to avoid possible drug interactions. Do not start, discontinue, or change the dosage of any medication without your doctor’s recommendation.
- Severe interactions: gemfibrozil, darolutamide, asmiditan, leniolisib, lopinavir, ritonavir
Contact your doctor, pharmacist, or health care provider for more information on drug interactions.
Always inform your doctor, pharmacist, or health care provider of all prescription and over-the-counter medications you use, including dosage information. Keep a list of this information available.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Pregnancy: No adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. No significant fetal harm shown in animal studies, but maternal and fetal body weight slightly reduced during organogenesis.
- Breastfeeding: Presence of selexipag or its metabolites in animal milk. Discontinue selexipag or breastfeeding due to potential adverse reactions in breastfed infants.
Additional Information
- Take selexipag as prescribed. Take any missed dose as soon as possible unless the next dose is within 6 hours.
- Swallow tablets whole. Do not split, crush, or chew.
- Keep selexipag out of reach of children.
- In case of overdose, seek medical help or contact Poison Control.
Summary
Selexipag is a medication used to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), a condition of high blood pressure in the arteries that carry oxygen-depleted blood from the heart to the lungs. Common side effects of selexipag include headache, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, reduced appetite, jaw pain, muscle pain, limb pain, joint pain, rash, flushing, anemia, drop in hemoglobin levels, and others. Do not take if breastfeeding.


