Contents
- 1 Hydroxyzine vs. Xanax
- 1.0.1 What are the side effects of hydroxyzine and Xanax?
- 1.0.2 What is the dosage of hydroxyzine vs. Xanax?
- 1.0.3 What drugs interact with hydroxyzine and Xanax?
- 1.0.4 Subscribe to MedicineNet’s Depression Newsletter
- 1.0.5 Are hydroxyzine and Xanax safe to use while pregnant and breastfeeding?
- 1.0.6 From
- 1.0.7 Summary
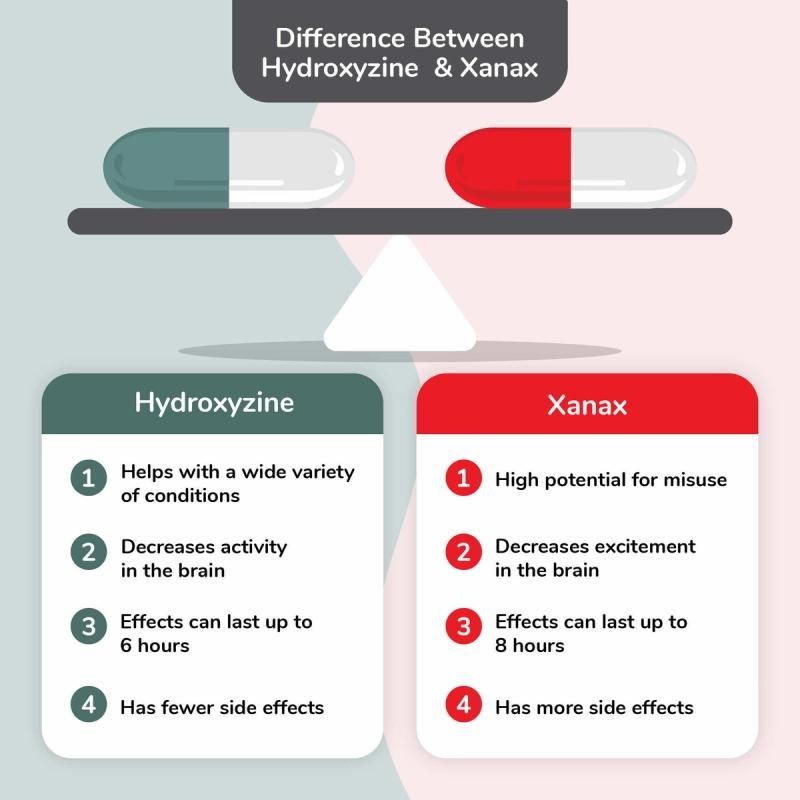
Hydroxyzine vs. Xanax
Hydroxyzine is an antihistamine with anticholinergic and sedative properties that is used to treat itching caused by various allergic reactions. It is also used to treat anxiety, tension, and induce sedation before or after anesthesia. Hydroxyzine can also treat nausea, vomiting, and alcohol withdrawal.
Xanax (alprazolam) is an anti-anxiety medication used for anxiety disorders and panic attacks. It is in the benzodiazepine drug family, which includes diazepam (Valium), clonazepam (Klonopin), lorazepam (Ativan), and flurazepam (Dalmane). Xanax and other benzodiazepines enhance the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that inhibits brain activity. Excessive brain activity is believed to cause anxiety and psychiatric disorders.
QUESTION
What are the side effects of hydroxyzine and Xanax?
Hydroxyzine side effects
The common side effects of hydroxyzine are:
- Sedation
- Tiredness
- Sleepiness
- Dizziness
- Disturbed coordination
- Drying and thickening of oral and respiratory secretions
- Stomach distress
Other important side effects include caution in persons with narrow-angle glaucoma, prostatic hypertrophy, hyperthyroidism, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, and asthma.
Xanax side effects
The most common side effects of Xanax at lower doses are:
Other side effects include:
- Memory problems
- Speech problems
- Constipation
- Changes in weight
- Addiction (dependency)
- Headache
- Constipation
- Dry mouth
What are the withdrawal symptoms of Xanax?
Withdrawal symptoms may occur with high doses given over prolonged periods. Abrupt discontinuation of alprazolam after prolonged use can lead to symptoms such as seizures. Therefore, patients on alprazolam for extended periods of time should slowly taper the medication under a doctor’s supervision.
What is the dosage of hydroxyzine vs. Xanax?
Hydroxyzine dosage
- Hydroxyzine takes effect 30 to 60 minutes after administration and lasts for 4 to 6 hours.
- The recommended dose for treating itching is 25 mg given 3 or 4 times daily orally or by injection.
- For sedation, the recommended dose is 50 to 100 mg orally or 25 to 100 mg by injection.
- Anxiety and tension are managed with 50 to 100 mg in 4 divided doses or 50-100 mg by injection in 4 or 6 divided doses.
- Alcohol withdrawal is treated with a 50-100 mg injection and may be repeated every 4 to 6 hours as needed.
- The dose for nausea and vomiting is 25 to 100 mg by injection.
- Hydroxyzine can be taken with or without food.
Xanax dosage
- The starting dose for treating anxiety is 0.25-0.5 mg 3 to 4 times daily using immediate-release tablets. The dose may be increased every 3-4 days to a maximum dose of 4 mg daily.
- The starting dose for treating panic attacks is 0.5 mg 3 times daily. Doses can be increased every 3-4 days but by no more than 1 mg daily.
- The effective dose for preventing panic attacks may be as high as 10 mg daily for some patients. The starting dose for using extended-release tablets to treat panic disorder is 0.5 mg once daily and the average dose is 3-6 mg once daily.
- Xanax may be taken with or without food.
What drugs interact with hydroxyzine and Xanax?
Hydroxyzine drug interactions
Hydroxyzine may intensify the sedating effects of alcohol and other drugs that cause sedation like benzodiazepines and narcotics. These drugs include diazepam, lorazepam, clonazepam, and alprazolam. Hydroxyzine also adds to the sedating effects of narcotic pain medications and tricyclic antidepressants. It can also intensify the drying effects of other medications with anticholinergic properties. When using these drugs, the dose of hydroxyzine may require reduction.
Xanax drug interactions
- Ketoconazole, itraconazole, nefazodone, cimetidine, and fluvoxamine increase concentrations in the blood of alprazolam and may increase its side effects.
- Xanax interacts with alcohol and medications that suppress brain activity, causing increased sedation.
- Carbamazepine and rifampin reduce the effect of alprazolam by increasing metabolism and elimination of alprazolam in the liver.
Subscribe to MedicineNet’s Depression Newsletter
By clicking "Submit," I agree to the MedicineNet Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy. I also agree to receive emails from MedicineNet and I understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet subscriptions at any time.
Are hydroxyzine and Xanax safe to use while pregnant and breastfeeding?
Hydroxyzine
- Limited studies of hydroxyzine in pregnant women suggest a relationship between its use in the first trimester of pregnancy and congenital abnormalities. Therefore, hydroxyzine should be avoided during the first trimester.
- It is unknown if hydroxyzine is excreted into breast milk. Antihistamines are generally not recommended during breastfeeding due to potential stimulation or seizures in newborns.
Xanax
- Benzodiazepines like alprazolam can cause fetal abnormalities and should not be used in pregnancy.
- Alprazolam is excreted in breast milk and can affect nursing infants. Therefore, women who are breastfeeding should not take alprazolam.
From
Mental Health Resources
- Bipolar Assessment: Can You Do More?
- Mental Health & STIs: What’s the Link?
- Navigating Life With Inoperable Lung Cancer
Featured Centers
- What Are the Best PsA Treatments for You?
- Understanding Biologics
- 10 Things People With Depression Wish You Knew
Summary
Hydroxyzine and Xanax (alprazolam) are used to treat anxiety. Hydroxyzine also treats itching caused by various allergic reactions, induces sedation prior to or after anesthesia, and treats nausea, vomiting, and alcohol withdrawal. Xanax also treats panic attacks. Hydroxyzine is an antihistamine with drying and sedative properties, while Xanax is an anti-anxiety medication in the benzodiazepine class.
Hydroxyzine and Xanax (alprazolam) are used to treat anxiety. Hydroxyzine also treats itching caused by various allergic reactions, induces sedation prior to or after anesthesia, and treats nausea, vomiting, and alcohol withdrawal. Xanax also treats panic attacks. Hydroxyzine is an antihistamine with drying and sedative properties, while Xanax is an anti-anxiety medication in the benzodiazepine class.