Contents
- 1 What Triggers Precordial Catch Syndrome?
- 1.0.1 What is Precordial Catch Syndrome?
- 1.0.2 What are the symptoms of precordial catch syndrome?
- 1.0.3 Causes and Risk Factors for Precordial Catch Syndrome
- 1.0.4 Is Precordial Catch Syndrome Life-Threatening?
- 1.0.5 How is Precordial Catch Syndrome Diagnosed?
- 1.0.6 Treatment Options for Precordial Catch Syndrome
- 1.0.7 Can You Prevent Precordial Catch Syndrome?
What Triggers Precordial Catch Syndrome?
Precordial catch syndrome is characterized by sharp, neurological pain in the chest, typically on the left side, triggered by deep inspiration. The exact cause is unclear but thought to be related to muscle spasms or irritation of intercostal nerves between the ribs.
Possible triggers of precordial catch syndrome include:
- Respiration: Deep or rapid breathing
- Exercise: Physical activity, especially intense or requiring deep breaths
- Emotions: Stress, anxiety, or other emotional states
Chest pain associated with precordial catch syndrome is usually benign and self-limiting. However, severe or persistent pain may signify a more serious condition and require immediate medical attention.
What is Precordial Catch Syndrome?
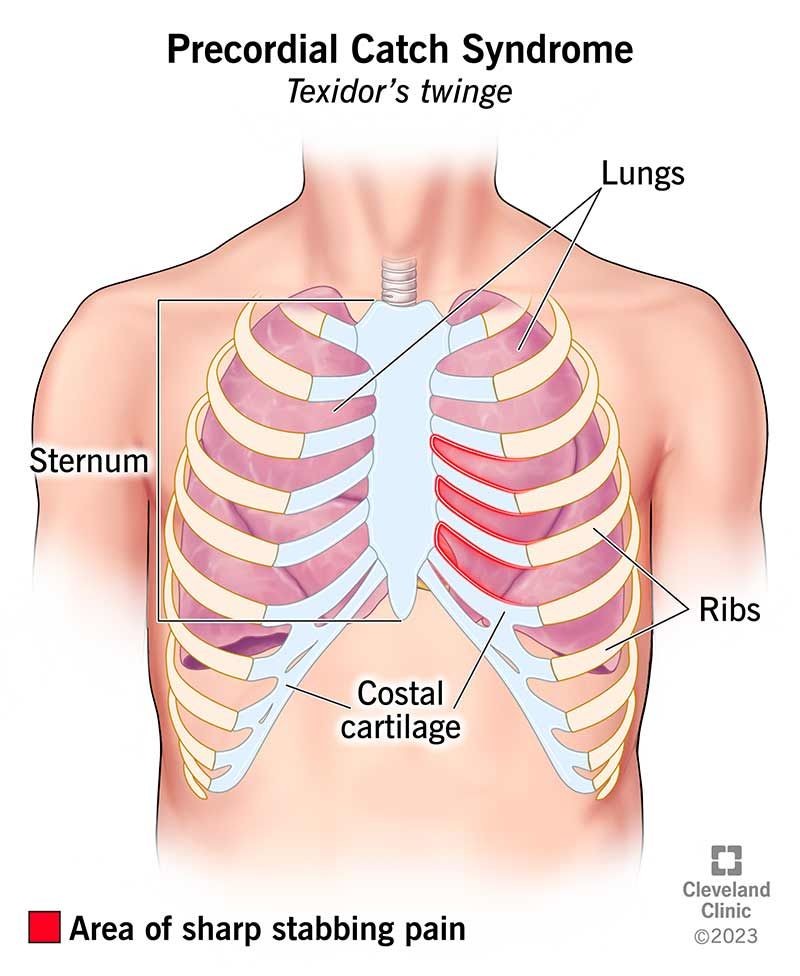
Precordial catch syndrome, also known as Texidor’s twinge, is a benign condition affecting children and adolescents. It causes sudden sharp, neurological pain on the left side of the chest, below the left nipple. The pain does not radiate but may be accompanied by a burning or tingling sensation. It results from muscle spasms in the chest wall, usually felt on the left side, just below the breastbone.
Precordial catch syndrome is a type of chest pain in the chest wall where intercostal nerves are located. It’s named after the physician Thomas Texidor who first described it. The pain is usually caused by irritation or compression of intercostal nerves, which supply sensation to the chest wall.
The specific cause of precordial catch syndrome is unclear but associated with:
- Muscle strain or spasms in the chest
- Rib fractures
- Nerve compression from conditions like herniated discs or tumors
- Irritation of the nerves
- Inflammation of the chest wall
- Gastrointestinal issues
- Stress
- Hormonal changes during puberty
While it can start at age six, it typically affects individuals in their late teens or early 20s. It usually occurs at rest or in a partially slouched position, such as when watching television on an old couch. It can even happen during simple activities like walking. Precordial catch syndrome never occurs during sleep and has no connection to meals. Episodes of chest pain may occur frequently or only once in a lifetime.
The pain lasts 30 seconds to a few minutes and may be relieved by deep breathing or changing body position. It may also be accompanied by chest tightness or pressure, lightheadedness, rapid heartbeat, and weakness.
QUESTION
What are the symptoms of precordial catch syndrome?
Precordial catch syndrome is intense pain lasting 30 seconds to three minutes or longer.
Unlike other chest pains, it’s not always associated with additional symptoms. However, some possible symptoms include:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Feeling of chest tightness or pressure
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating
- Light-headedness from shallow breathing due to pain
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- Fatigue
Some people experience worsening chest pain with deep breathing, while others find relief from pain with deep breathing or changing body position.
Precordial catch syndrome is a benign and self-limiting disorder of unknown origin occurring in healthy adolescents and young adults but can start earlier.
Causes and Risk Factors for Precordial Catch Syndrome
The exact cause is unknown, but possible causes include:
- Chest wall muscle spasms
- Nerve irritation in the chest
- Inflammation of the chest wall
- Gastrointestinal issues (acid reflux or indigestion causing chest pain)
- Stress (muscle tension due to emotional stress or anxiety can cause chest pain)
- Hormonal changes (more common in adolescents and young adults due to hormonal changes during puberty)
Risk factors for precordial catch syndrome
- Age: More common in children and adolescents, but can occur in adults
- Gender: More common in men than women
- Family history: Increased risk if other family members have had precordial catch syndrome
- Respiratory issues: Increased risk for people with asthma or bronchitis
- Cardiac issues: Increased risk for certain heart conditions
- Miscellaneous reasons: Sickle cell anemia, smoking, or substance abuse (cocaine addiction)
The specific cause of precordial catch syndrome is not identified. However, if you experience chest pain, it’s important to see a doctor to rule out serious issues.
Is Precordial Catch Syndrome Life-Threatening?
Precordial catch syndrome is not considered a serious or life-threatening condition. The pain is sharp and localized, lasting a few minutes. Although intense, it’s typically not a sign of a more serious problem and does not cause long-term damage.
Since chest pain can be a symptom of serious conditions like a heart attack, always consult a doctor to rule out possible underlying issues and receive appropriate treatment.
How is Precordial Catch Syndrome Diagnosed?
The diagnosis is typically based on symptoms and physical examination. After noting your medical history, your doctor may perform a physical exam to check for signs of chest, back, and abdomen pain or discomfort.
Other tests may be conducted to rule out potential causes:
- Electrocardiogram and echocardiogram: To check heart functionality and rule out other causes.
- Blood tests: To check for inflammation or infection.
- Imaging studies: Chest X-ray or CT scan may identify structural abnormalities causing chest pain.
Treatment Options for Precordial Catch Syndrome
Precordial catch syndrome typically doesn’t require treatment. However, options to alleviate symptoms include:
- Deep breathing: Taking slow, deep breaths to relax chest muscles (may increase chest pain for some).
- Changing position: Standing up or lying down to alleviate pain.
- Over-the-counter pain medication: Ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help relieve pain.
- Applying heat: Using a warm compress on the chest can relax muscles and ease pain.
- Avoiding triggers: Identify and avoid triggers that cause chest pain, such as certain foods or stress.
- Relaxation techniques: Yoga or meditation to reduce stress and alleviate symptoms.
- Behavioral therapy: Counseling or therapy for stress or anxiety-related precordial catch syndrome.
Can You Prevent Precordial Catch Syndrome?
Precordial catch syndrome is a benign and self-limiting condition with no known specific prevention methods. However, the following may reduce the risk of chest pain:
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: Balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption improve overall health and reduce chest pain risk.
- Managing stress: Engage in stress-reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, or counseling to reduce stress and anxiety triggers.
- Avoiding triggers: If specific triggers are known, such as certain foods or stress, try to avoid them.
- Staying hydrated and avoiding caffeine and nicotine: These substances can dehydrate the body and increase muscle tension, leading to chest pain.
By submitting, I agree to the MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.
By submitting, I agree to the MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.