Contents
4 Types of Allergic Reactions and Their Symptoms
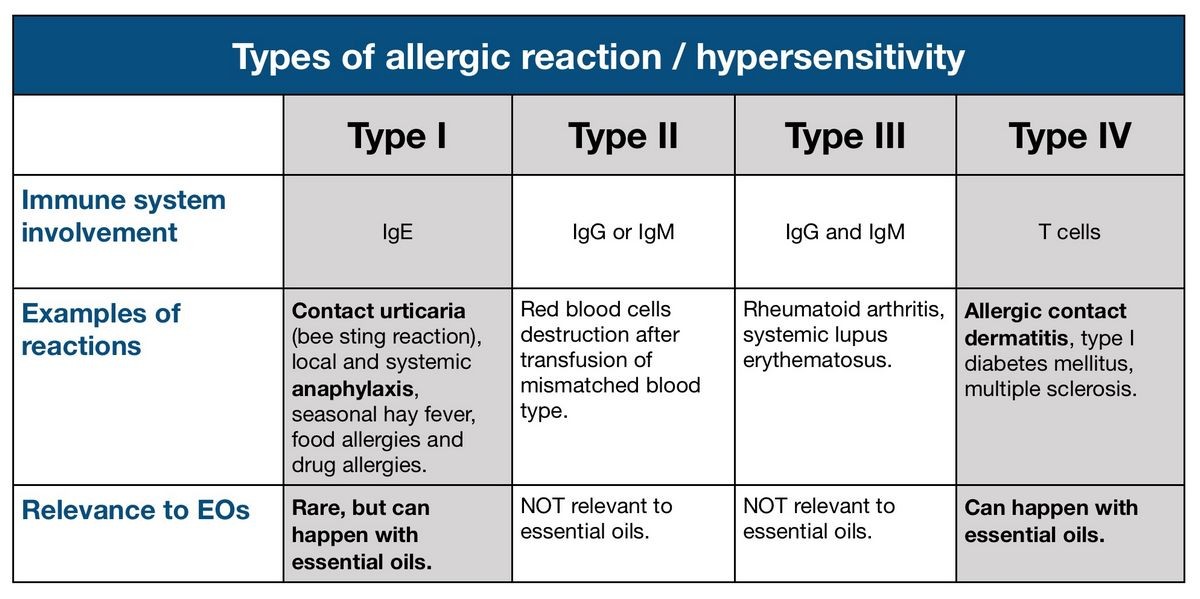
Allergists recognize four types of allergic reactions:
- Type I or anaphylactic reactions
- Type II or cytotoxic reactions
- Type III or immunocomplex reactions
- Type IV or cell-mediated reactions
Allergic reactions occur when your immune system abnormally responds to allergens such as pollen, dust, and certain foods. While harmless to most people, allergens can cause reactions in those who are allergic upon skin contact, inhalation, ingestion, or injection.
Allergic reactions can range from mild to severe, with symptoms appearing seconds to hours after exposure. They may be localized or affect the entire body. Examples include skin rashes from metal jewelry or cosmetics, and uncontrollable sneezing from dust or pollen exposure.
An allergic reaction is initiated when the body encounters an allergen, prompting the production of IgE antibodies. These antibodies bind to the allergen, leading to the release of chemicals like histamine that cause inflammatory symptoms such as itching, rashes, and sneezing.
The Four Types of Allergic Reactions
British immunologists Coombs and Gell classified allergic reactions into four types:
- Type I or anaphylactic reactions: Mediated by IgE antibodies, type I reactions result from exposure to allergens like pollen, animal dander, or certain foods. Symptoms include asthma, rhinitis, dermatitis, food allergies, conjunctivitis, and anaphylaxis.
- Type II or cytotoxic reactions: Mediated by IgG and IgM antibodies, type II reactions damage cells by activating the complement system. They can occur in conditions like autoimmune hemolytic anemia, immune thrombocytopenia, and autoimmune neutropenia.
- Type III or immunocomplex reactions: These reactions involve IgM and IgG antibodies that form immunocomplexes responsible for the reaction. Type III allergic reactions can be seen in certain diseases.
- Type IV or cell-mediated reactions: These delayed hypersensitivity reactions occur at least 24 hours after exposure to the allergen. They can take up to 72 hours to appear and are associated with long-term infectious diseases and skin sensitivity reactions.
Triggers of Allergic Reactions
Allergens that can trigger allergies include:
- Dust mites
- Animal/pet dander
- Pollen
- Bee/wasp stings
- Certain medications
- Certain foods
- Mold
- Latex
- Certain metals
- Some plants
Symptoms of an Allergic Reaction
If you experience the following symptoms, it is likely that you are having an allergic reaction:
- Tingling, itching, and swelling of the lips, face, and tongue
- Swelling in other parts of the body
- Trouble breathing and wheezing
- Nasal congestion and runny nose
- Hives and skin redness
- Abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea
- Dizziness and vomiting
- Itchy, watery eyes and sneezing
- Stomach cramps and cough
Symptoms such as difficulty breathing, hives, throat tightness, and low blood pressure can indicate a severe, life-threatening anaphylactic reaction, requiring immediate medical attention.
Treatment and Prevention of Allergies
Treating allergies involves identifying and avoiding allergens. If avoidance is not possible, treatment options may include allergy shots and medications like antihistamines. For life-threatening allergies, an epinephrine auto-injector may be prescribed.
Preventing Allergies
To prevent allergies:
- Identify your allergens, such as dust mites, dander, mold, pollen, and certain foods.
- Control or eliminate the allergen, taking precautions with pets, dust mites, pollen, and mold.
- Avoid touching or rubbing your nose and wash your hands frequently.
- Protect yourself from allergens by wearing sunglasses and a hat.
Reference: Medscape Medical